# Release Notes
Here you will find the latest information about releases of the jSparrow Eclipse plugin.
# 4.19.0 05.04.2024
The 119th refactoring rule and one additional jSparrow marker are shipped with jSparrow 4.19.0. The new rule in-lines local variables which are returned or thrown immediately after their declaration.
# New Rule
# Inline Local Variables
This rule is used to in-line local variables which are used exactly once in a return- or in a throw statement.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds one additional marker for the following rule:
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 95.
# 4.18.0 07.07.2023
The 118th refactoring rule and 2 additional jSparrow markers are shipped with jSparrow 4.18.0. The new rule replaces simple if-statements by equivalent constructs where the ternary operator is used.
# New Rule
# Use Ternary Operator
This rule is used to replace if-statements by equivalent statements using the ternary operator in cases where such a replacement is reasonable.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 2 additional markers for the following rules:
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 94.
# 4.17.0 31.05.2023
# New "Select Java Sources To Refactor" Dialog
In this release we have introduced a new dialog. This dialog offers the developer a comfortable user interface to select all Java sources which he wants to refactor with jSparrow rules.
# 4.16.0 23.03.2023
# Free License without Registration
In this release we have abolished the need to register for a free trial version. From now on 20 of our most liked rules and additionally also our markers can be applied without any License immediately after the installation in Eclipse.
# 4.15.0 23.02.2023
# UI Improvements
In this release we have once again improved the user experience of our jSparrow Eclipse Plugin. There is a better handling of the UI in connection with the refactoring process.
# 4.14.1 10.01.2023
# Hotfix Release
This release fixes the issues for the usage of jSparrow on eclipse 2022-12.
# 4.14.0 30.12.2022
# UI Improvements
This release offers an improved user experience of our jSparrow Eclipse Plugin. We have changed the appearance of the UI for the rule selection and the licensing process.
# 4.13.1 26.10.2022
# Hotfix Release
This hotfix release fixes a JNA issue related to license validation.
# Fixed Bugs
# Cannot initialize class JNA Native
- Fixed a license validation issue on some Eclipse versions started with JDK 11+.
# 4.13.0 26.09.2022
The 117th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 4.13.0. It replaces complex cascading if statements by switch expressions or switch statements with switch labeled rules which have been introduced in Java 14.
# New Rules
# Replace Set.removeAll With ForEach
Calling the method 'removeAll' on a Set with a List as invocation argument may lead to performance problems due to a possible O(n^2) complexity. This rule replaces such invocations. For example, the invocation 'mySet.removeAll(myList);' is replaced by 'myList.forEach(mySet::remove);'.
# Replace Wrong Class for Logger
If a given logger is initialized with a class that is different from the class where it is declared, then this rule will replace the wrong initialization argument with the correct one. For example, if a logger for the class 'Employee' is initialized with 'User.class', then the argument of the initialization will be replaced by 'Employee.class'.
# Replace Multi Branch If By Switch
In Java 14, the switch expressions turned into a standard feature. This rule replaces multi-branch if statements by corresponding switch expressions or switch statements with switch labeled rules. Because this rule removes a lot of redundant parts of code, readability is improved.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 2 markers for the following rules:
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 92.
# 4.12.0 23.06.2022
The 114th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 4.12.0. The new rule encourages the usage of Spring dedicated annotations for creating web controllers.
# New Rule
# Replace Request Mapping Annotation
The Spring Framework 4.3 introduced some composed annotations like '@GetMapping', '@PostMapping', etc... as an alternative of @RequestMapping(method=...) (opens new window) for annotating HTTP request handlers.
Accordingly, this rule replaces the @RequestMapping annotations with their equivalent dedicated alternatives, for example, @RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET) is replaced by @GetMapping(value = "/hello").
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds one marker for the following rule:
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 90.
# 4.11.0 19.05.2022
The 113th refactoring rule and 13 additional jSparrow markers for existing rules are shipped with jSparrow 4.11.0. The new rule encourages the removal of redundant resource 'close()' invocations.
# New Rule
# Remove Redundant Close
This rule is used to remove redundant 'close()' invocation statements on resources which are declared in the header of try-with-resource statements.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 13 additional markers for the following rules:
- Add Braces to Control Statements
- Remove Deprecated Date Constructs
- Replace Nested Loops with flatMap
- Replace static final Collections with Collections.unmodifiable...()
- Use Portable Newline
- Use StringUtils Methods
- Use Predefined Standard Charset
- Use Dedicated AssertJ Assertions
- Replace JUnit assertThat with Hamcrest
- Replace JUnit Expected Annotation Property with assertThrows
- Replace JUnit ExpectedException with assertThrows
- Replace JUnit Timeout Annotation Property with assertTimeout
- Remove Redundant Close
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 89.
# 4.10.0 25.04.2022
The 112th refactoring rule and 10 additional jSparrow markers for existing rules are shipped with jSparrow 4.10.0. The new rule encourageS the removal of unused types.
# New Rule
# Remove Unused Types
This rule finds the type declarations that are never used and removes them.
Users can choose to remove types that are only used in test sources, together with their corresponding tests.
Any annotation except for @Deprecated and @SuppressWarnings prevents the type declaration from being considered as unused.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 10 additional markers for the following rules:
- Make Fields and Variables Final
- Use @Override Annotation
- Use equals() on Primitive Objects
- Remove Collection::addAll
- Remove Explicit Call To super()
- Remove Unnecessary Thrown Exceptions on Method Signatures
- Reorder Modifiers
- Remove Lambda Expression Braces
- StringBuffer() to StringBuilder()
- Use Offset Based String Methods
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 76.
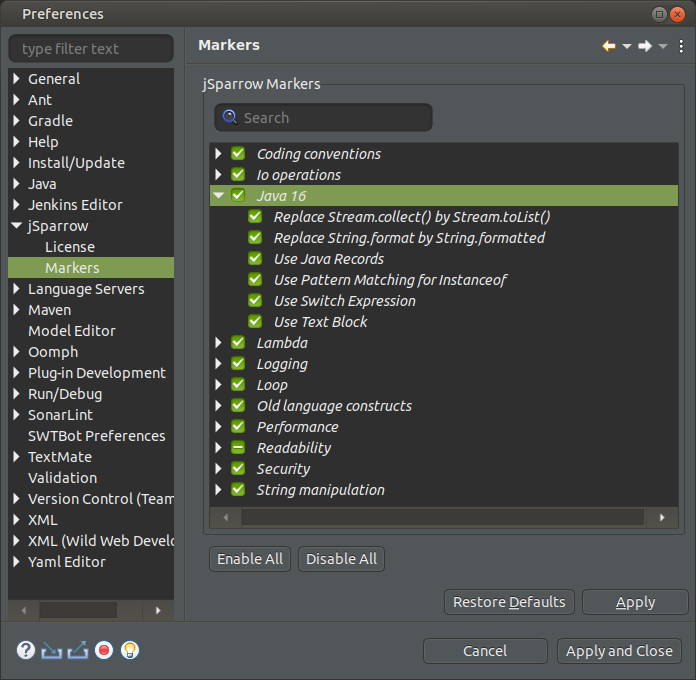
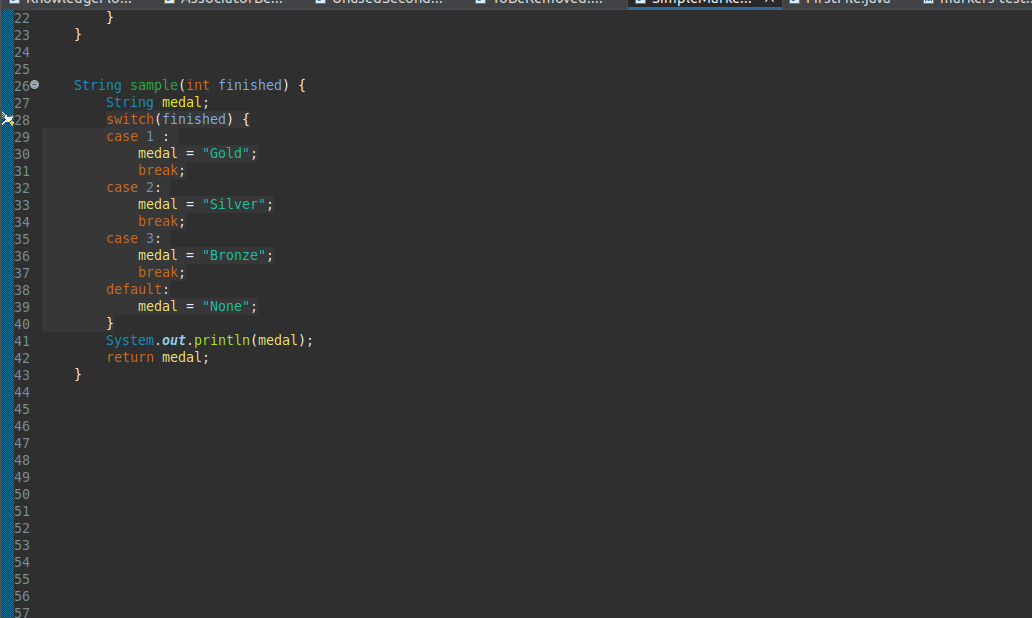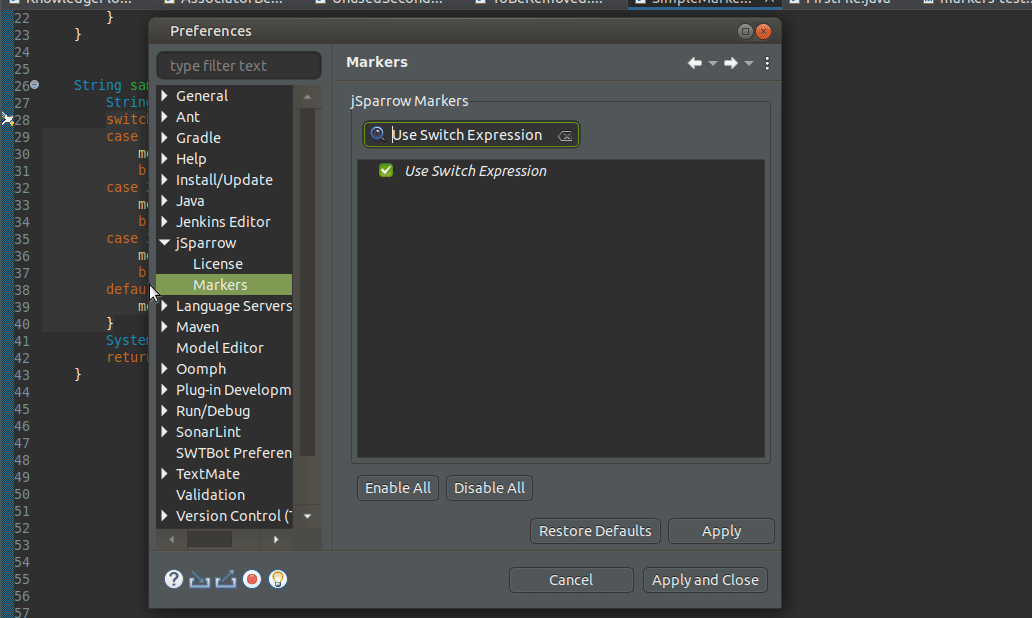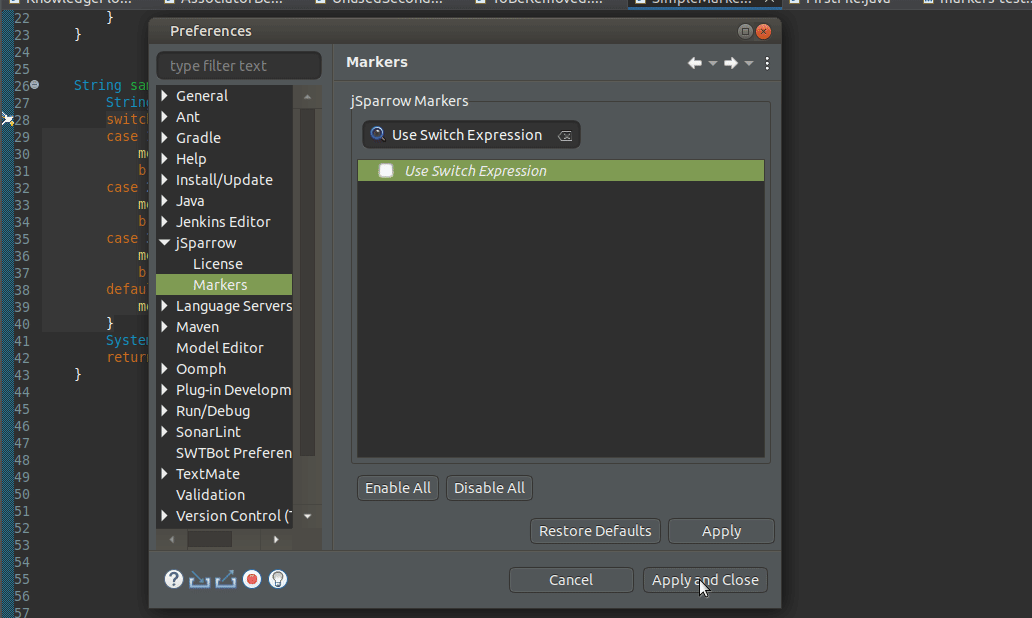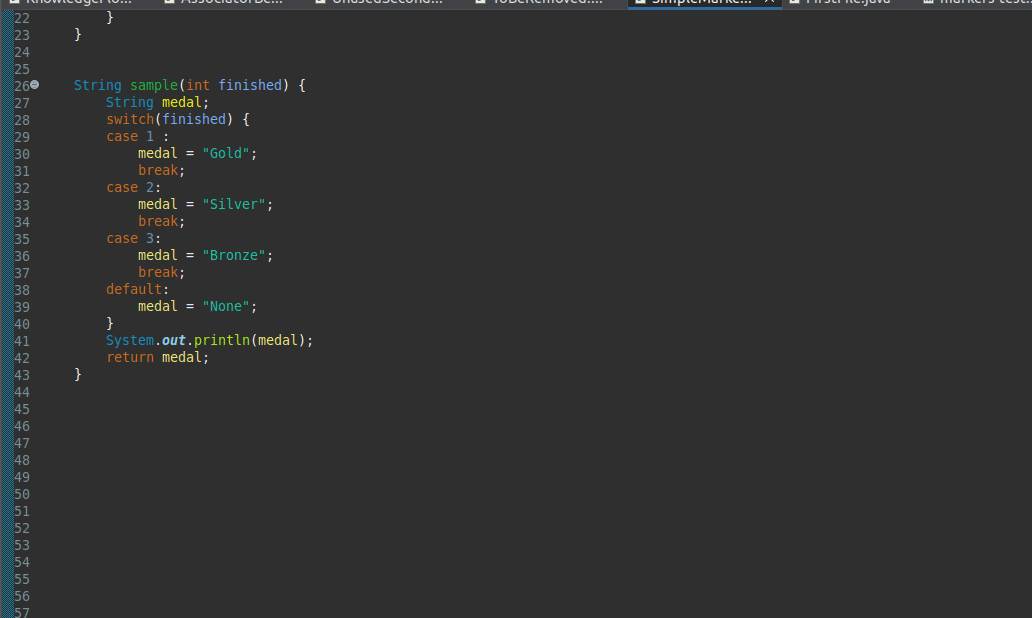
# jSparrow Markers Preference Page
The jSparrow Markers preference page is extended with a search field that allows users to find jSparrow markers by their name and category:
# Quick-fix to Deactivate jSparrow Markers
All jSparrow markers are extended with a quick-fix that allows users to deactivate markers. This quick-fix, automatically opens the preference page and searches for the corresponding marker by its name:
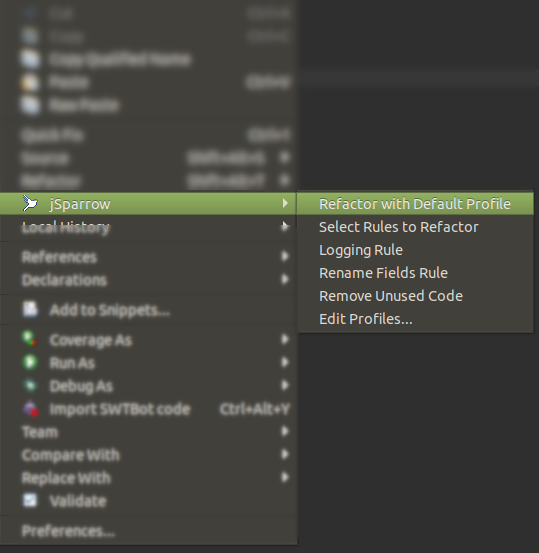
# Run jSparrow with the Default Profile
The jSparrow context menu is extended with new entires:
- 'Refactor with Default Profile' - starts jSparrow in the selected sources with the rules defined in the default profile. In this way, the select rules wizard is skipped and the preview wizard will open immediately after computing refactoring is over.
- 'Edit profiles...' - opens the jSparrow preference page for editing profiles and selecting the default profile.
# 4.9.0 17.03.2022
The 111th refactoring rule and 10 additional jSparrow markers for existing rules are shipped with jSparrow 4.9.0. The new rules encourage the removal of unused methods and local variables.
# New Rules
# Remove Unused Methods
This rule finds the method declarations that are never used and removes them.
Users can choose to remove methods that are only used in test sources, together with their corresponding tests.
Any annotation except for @Deprecated and @SuppressWarnings prevents the method declaration from being considered as unused.
# Remove Local Variables
This rule finds declarations of local variables that are never used and removes them.
Reassignments as well as increment and decrement operations are not counted as active usages.
Any annotation except for @Deprecated and @SuppressWarnings prevents the local variable from being considered as unused.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 10 additional markers for the following rules:
- Collapse If Statements
- Use Guard Condition
- Split Multiple Variable Declarations
- Remove Inherited Interfaces from Class Declaration
- Remove Double Negations
- Remove Unnecessary Semicolons
- Remove Modifiers in Interface Properties
- Remove toString() on String
- Replace String Format by Formatted
- Replace Collection.sort with List.sort
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 66.
# 4.8.0 17.02.2022
The 109th refactoring rule and 15 additional jSparrow markers for existing rules are shipped with jSparrow 4.8.0. The new rule encourages the removal of unused fields.
# New Rule
# Remove Unused Fields
This rule finds the field declarations that are never used and removes them.
Reassignments in the same or in external Java files are not counted as active usages.
A dedicated configuration wizard allows users to choose whether to remove fields whose initializers may cause side effects.
Any annotation except for @Deprecated and @SuppressWarnings prevents the field declaration from being considered as unused.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 15 additional markers for the following rules:
- Replace Assignment with Compound Operator
- Use Files.newBufferedReader
- Use Files.newBufferedWriter
- Use Files.writeString
- Use BufferedReader::lines
- Use Optional::filter
- Use Optional::ifPresent
- Use Optional::ifPresentOrElse
- Use Optional::map
- Create Temp Files Using Java NIO
- Reuse Random Objects
- Use SecureRandom
- Use Parameterized JPA Query
- Use Parameterized Query
- Use Parameterized LDAP Query
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 56.
# 4.7.0 20.01.2022
The 108th refactoring rule and 21 additional jSparrow markers for existing rules are shipped with jSparrow 4.7.0. The new rule encourages the usage of dedicated AssertJ assertions.
# New Rule
# Use Dedicated AssertJ Assertions
AssertJ contains a rich API for writing specific assertions about different types of objects. Making use of the appropriate dedicated methods when writing certain assertions will simplify the test code and improve the corresponding failure messages. This rule finds AssertJ assertions that can be simplified and replaces them with equivalent dedicated assertions.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 21 additional markers for the following rules:
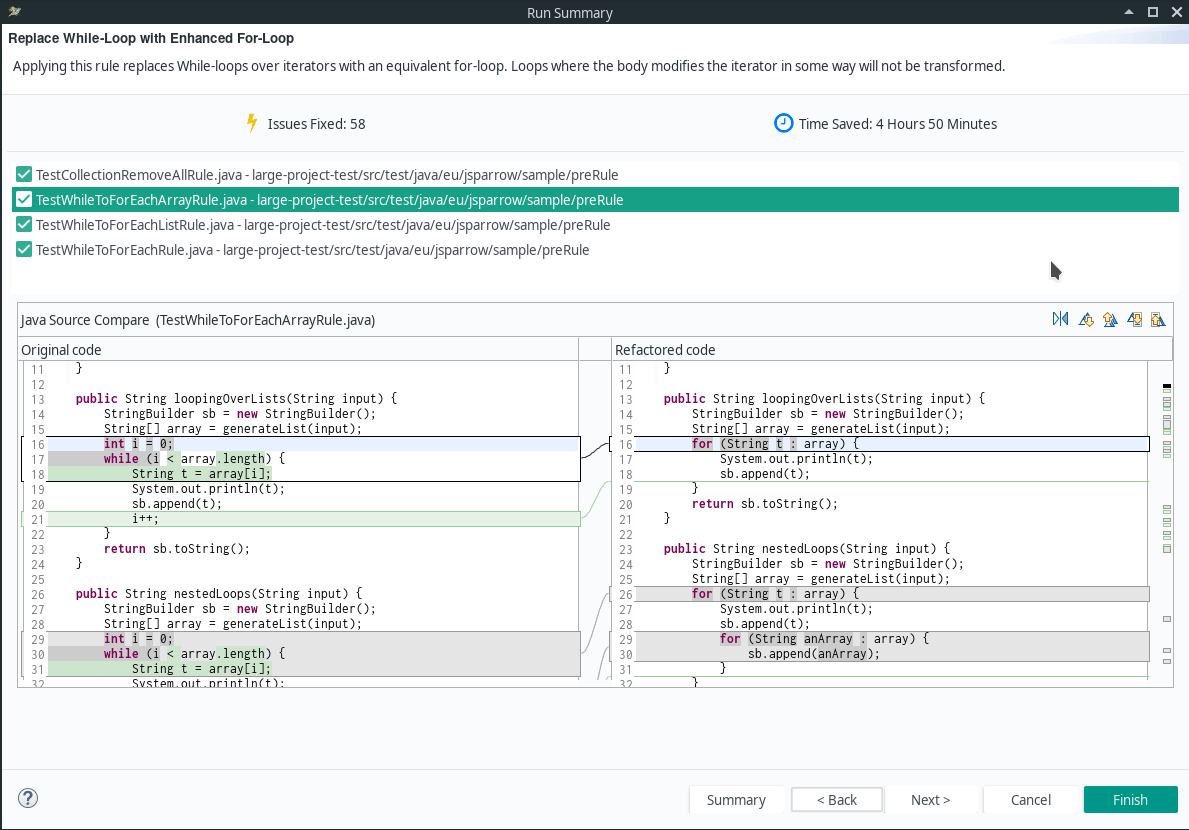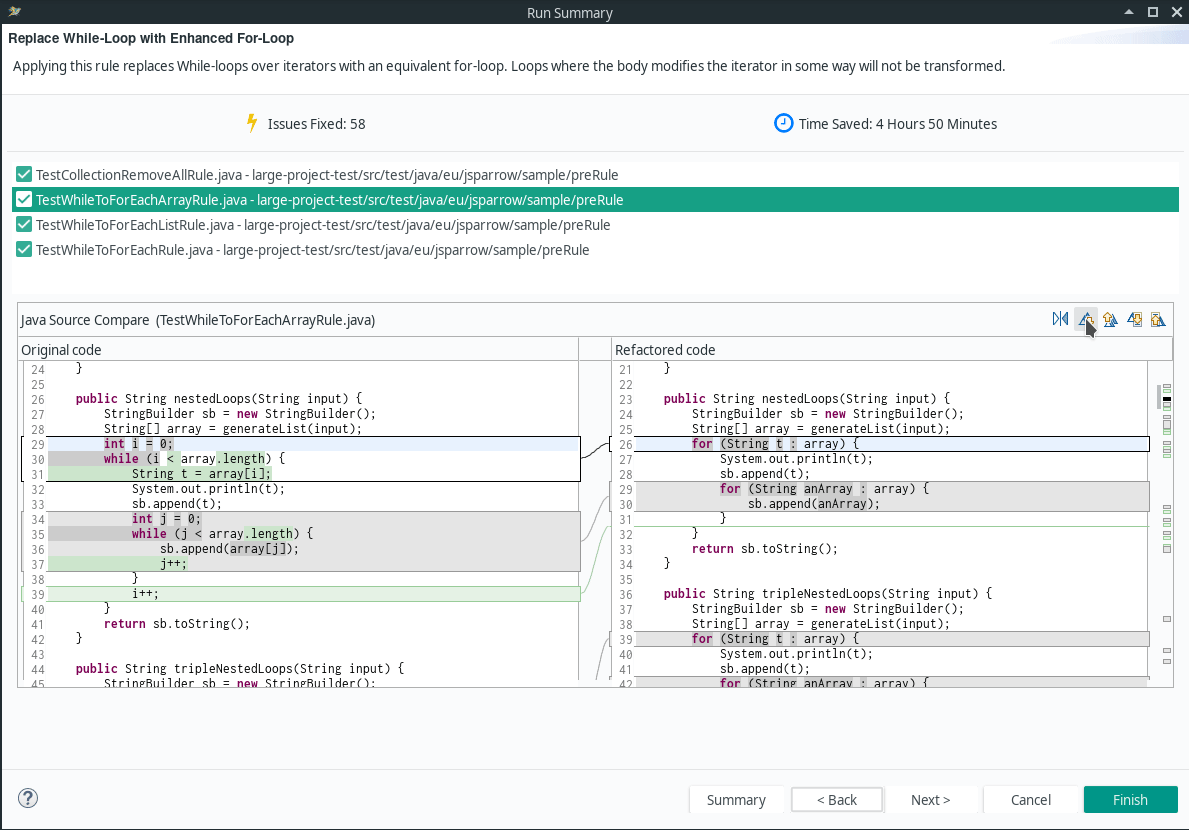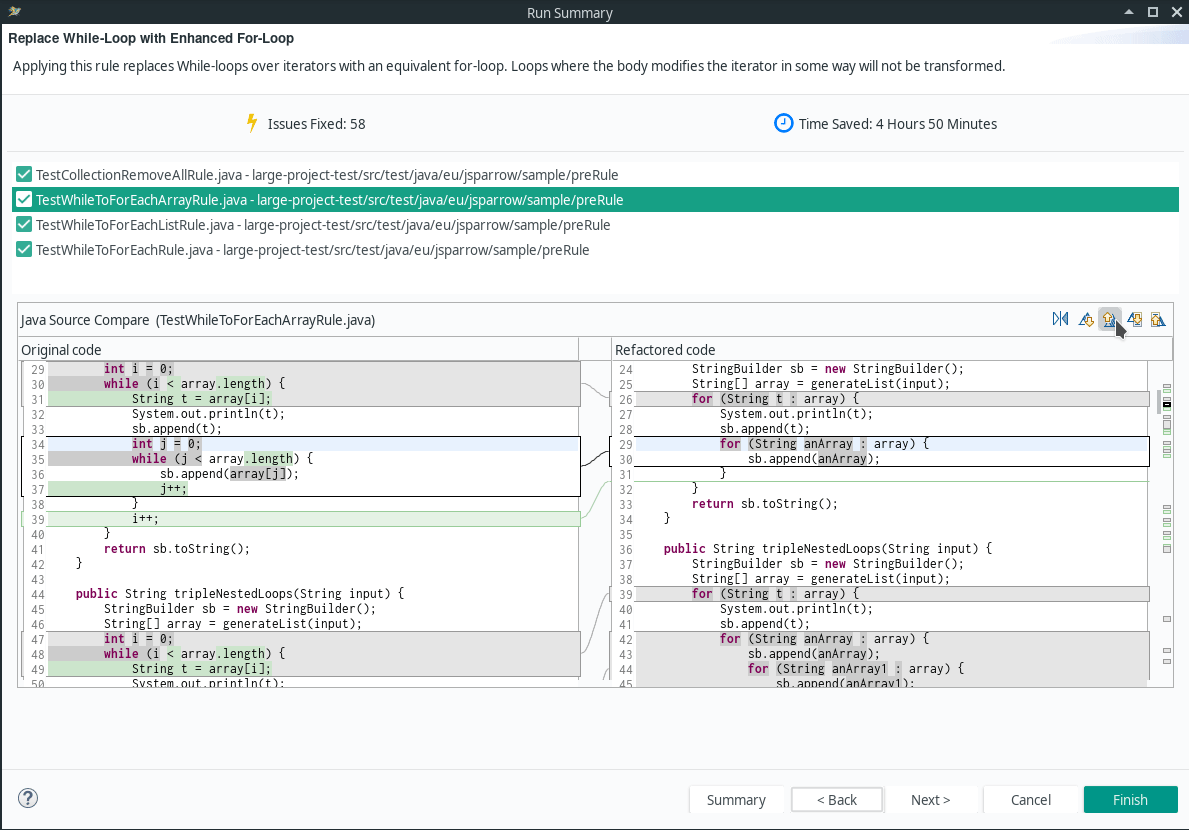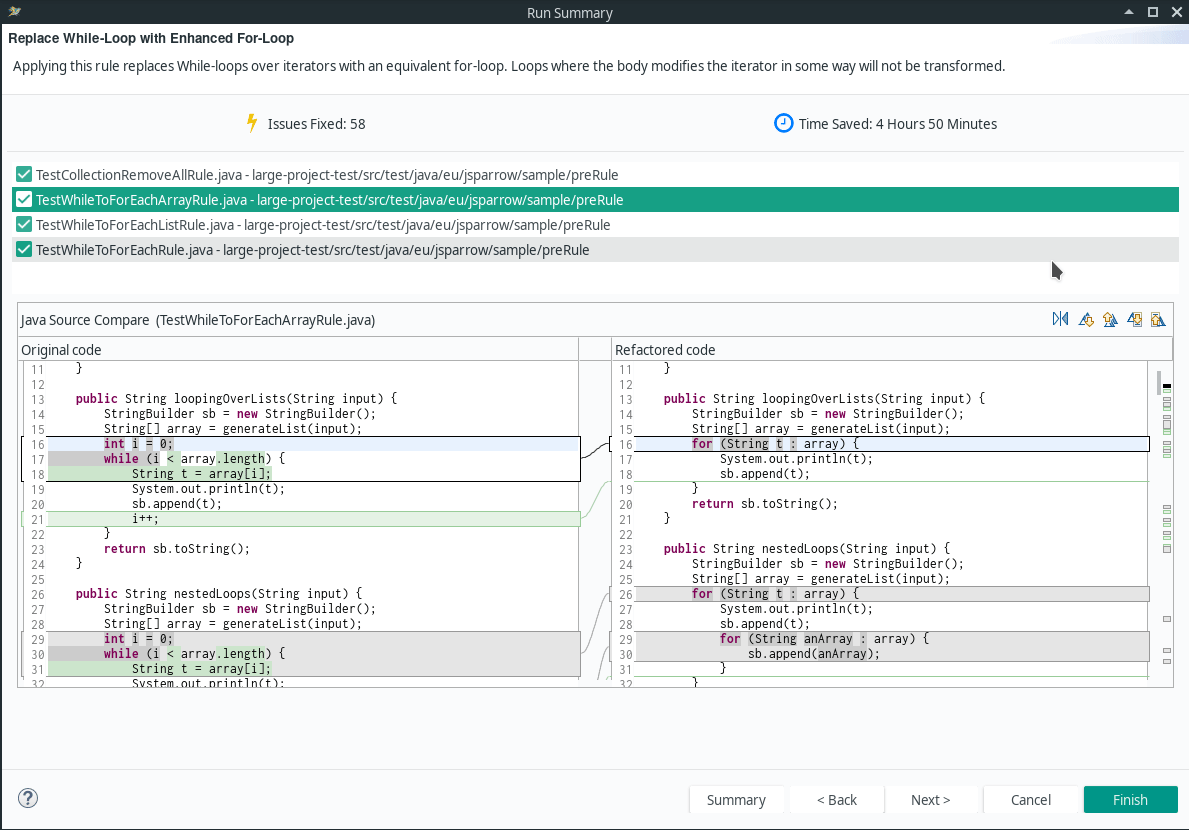
- Replace For-Loop with Enhanced-For-Loop
- Replace While-Loop with Enhanced For-Loop
- Replace For-Loop with Stream::collect(Collectors.joining())
- Use String Join
- Use Multi Catch
- Use Try-With-Resource
- Use Arrays Stream
- Use Stream::filter
- Use Stream::map
- Use Stream::collect
- Use Factory Methods for Collections
- Replace Stream Collect By ToList
- Replace For-Loop with Stream::Match
- Replace For-Loop with Stream::findFirst
- Replace For-Loop with Stream::forEach
- Replace For-Loop with Stream::sum
- Replace For-Loop with Stream::takeWhile
- Use Text Block
- Use Switch Expression
- Use Java Records
- Use Pattern Matching for Instanceof
Thus, setting the total number of available jSparrow Markers to 41.
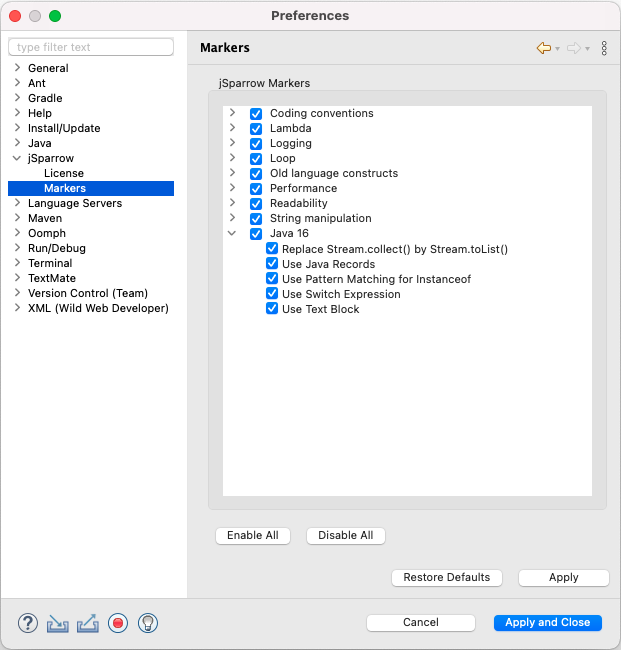
# jSparrow Markers Preference Page
The jSparrow Markers preference page is redesigned to group the markers by tags:
# Fixed Bugs
# Use Stream::map
- Avoids duplicating the
finalmodifier in the parameter declaration of the extracted Stream or Optional map.
# 4.6.0 16.12.2021
The winter solstice jSparrow 4.6.0 release extends the rule set with two new refactoring rules, introduces the Pay-Per-Use license model, and adds 10 more jSparrow Markers.
# New Rules
# Chain AssertJ AssertThat Statements
AssertJ encourages writing fluent test cases by chaining the assertions that target the same object instead of invoking assertThat (opens new window) multiple times.
This rule replaces consecutive AssertJ assertThat invocations targeting the same object with an assertion chain.
Thus, eliminating some redundant code and increasing the readability of test cases.
# Shift AssertJ Description Before Assertion
AssertJ provides methods for setting descriptions or error messages of assertions, e.g.: as (opens new window), describedAs (opens new window), withFailMessage (opens new window), and overridingErrorMessage (opens new window). These methods should always be invoked before the actual assertion they intend to describe, otherwise, they have no effect. This rule, swaps the invocation of the assertion methods with the invocation of the methods setting descriptions or the error messages for the corresponding assertions.
# Pay-Per-Use License Model
This is a new licensing model that jSparrow offers in addition to the existing Floating and Node-Locked models. Users can get pre-paid packages (opens new window) of 675 or 1350 credits. One unit of credit represents an estimation of one minute remediation cost.
Credit Calculation
Every jSparrow rule has an estimation of the remediation cost in minutes for one resolved issue. Resolving one issue with a certain rule, reduces the available credit with the amount of the remediation cost for that rule. Exceptions are rules having a remediation cost higher than 20, as they charge only 20 units of credit for every resolved issue.
# More jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduced Markers since version 4.0.0. This release adds 10 additional markers for the following rules:
The following rules will automatically generate markers in the Java files that are opened in the editor:
- Avoid Concatenation in Logging Statements
- Insert Break Statements in For-loops
- Remove Explicit Type Argument
- Remove Unused Parameters in Private Methods
- Remove Redundant Type Cast
- Replace indexOf() with contains()
- Replace Map::get by Map::getOrDefault
- Replace put(..) with putIfAbsent(..)
- Replace removeAll() with clear()
- Use Collections Singleton List
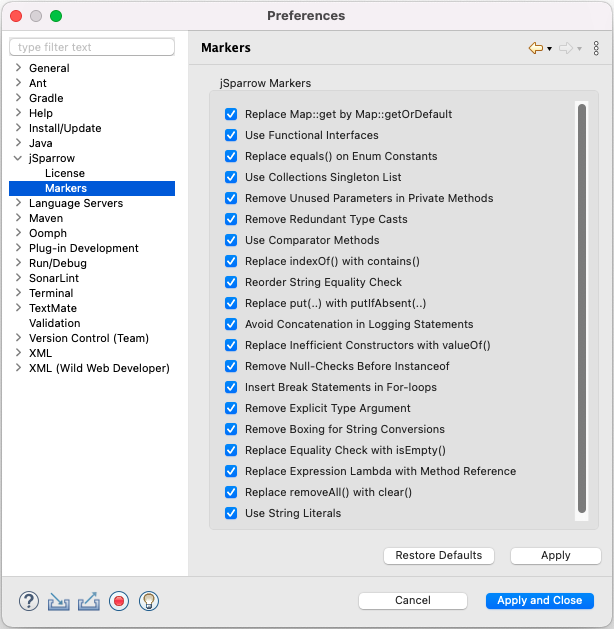
# jSparrow Markers Preference Page
The jSparrow Markers preference page allows users to choose the set of markers that automatically appear in the opened Java editors.
# 4.5.0 18.11.2021
The 105th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 4.5.0. The new rule supports Java Record classes introduced in Java 16.
# New Rule
# Use Java Records
Since Java 16, record classes are a new kind of class in the Java language. Record classes help to model plain data aggregates with less ceremony than normal classes. This rule replaces the declarations of local classes, inner classes, and package private root classes with record class declarations.
# 4.4.0 21.10.2021
The 104th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 4.4.0. The new rule supports an extension of the Stream API introduced in Java 16.
# New Rule
# Replace Stream Collect By ToList
Java 16 introduced Stream.toList() (opens new window) as a shorthand method for converting a Stream into an unmodifiable List.
This rule replaces invocations of collect(Collectors.toUnmodifiableList()) on a stream by the new method stream.toList().
# Fixed Bugs
# Use Files.writeString
- Files.writeString should be completely unwrapped from the try-catch statements in some cases where the catch clause is missing.
# Replace JUnit 3 Test Cases
- Avoids transformation in some cases where the
TestCasetype is explicitly used is the main method of the test class.
# 4.3.0 16.09.2021
The autumn release of jSparrow 4.3.0 introduces 3 refactoring rules. This extends the total number of jSparrow rules to 103. The new rules support some new features in Java 14 and 15.
# New Rules
# Use Switch Expression
This rule replaces the traditional switch-case statements with switch-case expressions, which turned to standard feature in Java 14.
# Use Text Block
This rule replaces multiline String concatenation expressions with Text Block String literals, which turned to standard feature in Java 15.
# Replace String Format by Formatted
This rule replaces the static invocations of String.format(String format, Object... args) (opens new window) by invocations of the new instance method String.formatted(Object... args) (opens new window).
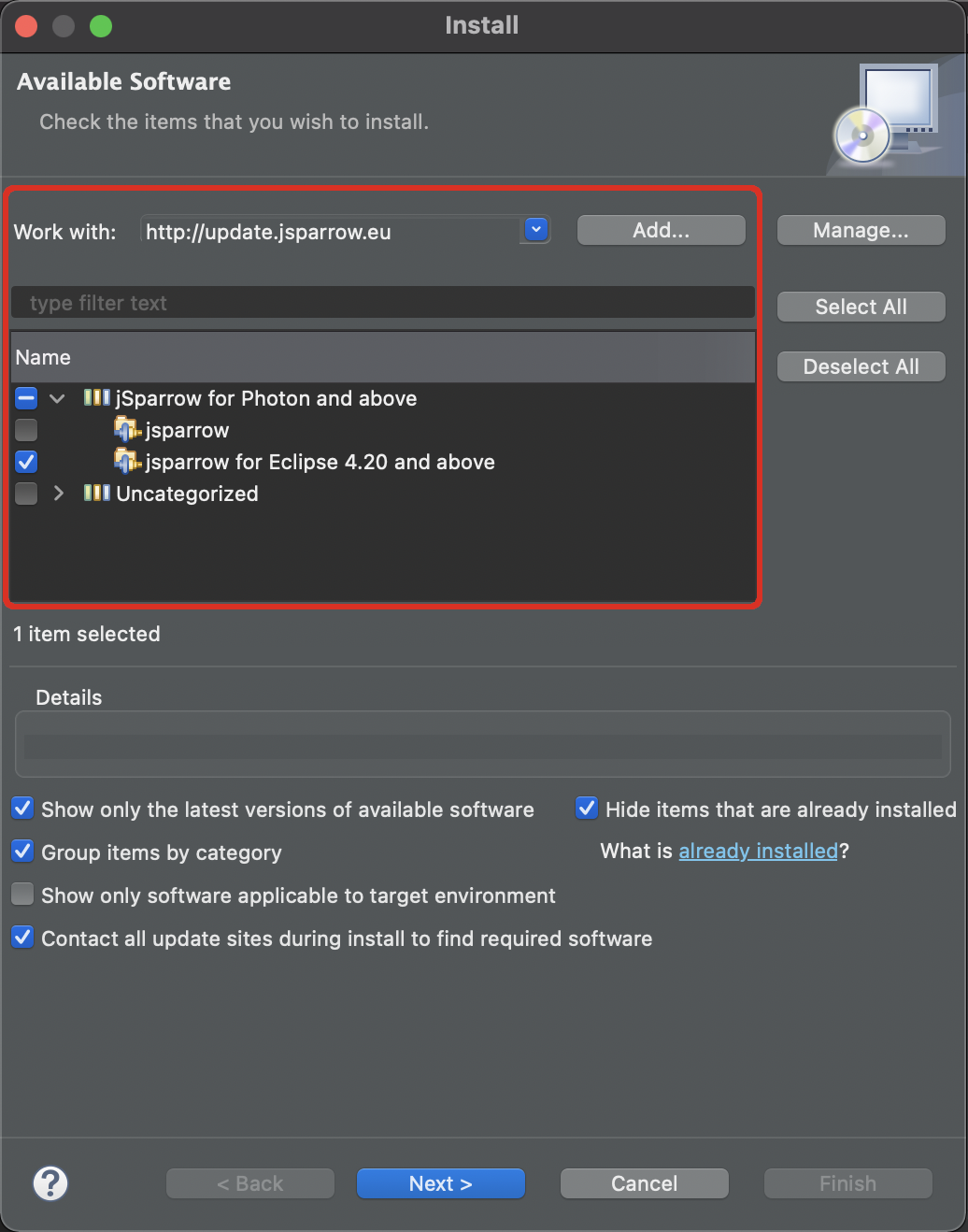
# Installation
The jSparrow rules that make use of the new language features, e.g., Pattern Matching for Instanceof, Text Blocks, or Switch Expressions are available for Eclipse 2021-06 (4.20) and later. Choose 'jSparrow for Eclipse 4.20 and above' in the installation wizard to get jSparrow with the complete rule-set for the latest Java versions.
# 4.2.0 19.08.2021
The 100th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 4.2.0. The new rule supports upgrading to Java 16.
# New Rule
# Use Pattern Matching for Instanceof
The new rule replaces instanceof expressions by Pattern Matching for instanceof (opens new window) introduced in Java 16.
# 4.1.0 15.07.2021
The 99th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 4.1.0. The new rule replaces JUnit 3 test cases with JUnit 4 or JUnit Jupiter.
# New Rule
# Replace JUnit 3 Test Cases
This rule migrates JUnit 3 tests to either JUnit JUpiter or JUnit 4 depending on the most up-to-date JUnit version available in the classpath.
# 4.0.0 17.06.2021
The new jSparrow 4.0.0 major release introduces jSparrow Markers and adds 3 more rules to the rule set, thus increasing the total number of refactoring rules to 98.
# jSparrow Markers
jSparrow introduces resource markers for highlighting and providing quick-fixes for issues and code smells.

The following rules will automatically generate markers for the Java files that are opened in the editor:
- Replace equals() on Enum Constants
- Use Functional Interfaces
- Replace Inefficient Constructors with valueOf()
- Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference
- Remove Boxing for String Conversions
- Replace put(..) with putIfAbsent(..)
- Remove Null-Checks Before Instanceof
- Reorder String Equality Check
- Use Comparator Methods
- Replace Equality Check with isEmpty()
jSparrow Markers are not persisted on disk. They are generated and deleted when a Java file is opened and closed.
# New Rules
# Use Dedicated Assertions
Replaces boolean assertions (e.g., assertTrue and assertFalse) with the corresponding dedicated assertions when testing for equality or null values.
For example, assertTrue(a.equals(b)) can be replaced by assertEquals(a, b). Similarly, assertSame, assertNotSame, assertNull, or assertNotNull can be used instead of assertTrue or assertFalse.
# Replace JUnit Assumptions with Hamcrest JUnit
This rule replaces the JUnit 4 assumptions assumeThat (opens new window), assumeNoException (opens new window), and assumeNotNull (opens new window) by the equivalent Hamcrest JUnit assumption MatcherAssume.assumeThat (opens new window).
# Replace JUnit 4 Category with JUnit Jupiter Tag
This rule replaces JUnit 4 @Category (opens new window) annotations with one or more JUnit Jupiter @Tag (opens new window) annotations.
# 3.30.0 20.05.2021
The 95th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.30.0. The new rule replaces JUnit 4 assumption methods with Jupiter assumptions.
# New Rule
# Replace JUnit 4 Assumptions with JUnit Jupiter
This rule contributes to a stepwise transition to JUnit 5 by replacing the JUnit 4 assumption methods assumeTrue and assumeFalse by their equivalent JUnit 5 ones.
# 3.29.0 15.04.2021
The 94th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.29.0. The new rule replaces JUnit assertThat with Hamcrest assertThat.
# New Rule
# Replace JUnit assertThat with Hamcrest
The JUnit Assert.assertThat method is deprecated. Its sole purpose is to forward the call to the MatcherAssert.assertThat method defined in Hamcrest 1.3. Therefore, it is recommended to directly use the equivalent assertion defined in the third party Hamcrest library.
# Enhancements
# Replace JUnit 4 Assertions with JUnit Jupiter
- Extends the rule coverage by allowing the replacement of JUnit 4 assertion
Assert.assertThrows(opens new window) with its equialent Jupiter alternativeAssertions.assertThrows(opens new window).
# 3.28.0 18.03.2021
The 93rd refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.28.0. The new rule migrates JUnit 4 assertions to JUnit 5.
# New Rule
# Replace JUnit 4 Assertions with JUnit Jupiter
This rule contributes to a stepwise transition to JUnit 5 by replacing the JUnit 4 assertion methods by the equivalent JUnit 5 ones.
# Fixed Bugs
# Replace JUnit Expected Annotation Property with assertThrows
- Extends the rule coverage by allowing non-final fields to be referenced in the lambda expressions used in
assertThrows.
# 3.27.1 03.03.2021
# Hotfix Release
This hotfix release fixes bugs on two refactoring rules.
# Fixed Bugs
# Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference
- Fixed an issue that could occur when lambdas are used as parameters of a vararg method invocation.
# Remove Redundant Type Casts
- Fixed an issue where compilation errors in overloaded methods could cause a NullPointerException.
# 3.27.0 18.02.2021
The 92nd refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.27.0. The new rule migrates JUnit 4 tests to JUnit 5.
# New Rule
# Replace JUnit 4 Annotations with JUnit Jupiter
This rule offers a stepwise transition to JUnit 5 by replacing JUnit 4 annotations @Test, @Ignore, @Before, @BeforeClass, @After, and @AfterClass with their corresponding Jupiter alternatives.
# Fixed Bugs
# Replace Expression Lambda With Method Reference
- Prevents transforming lambdas to method references in some cases where lambda parameters have more specific types than the functional interface expected on the context.
# Use Multi Catch
- Prevents collapsing the catch clauses if the caught exception invokes a method which is not defined in the least upper-bound of all combined exceptions.
# Remove Collection::addAll
- Prevents transformation in some cases where there is no constructor defined for expecting a collection.
# Remove Redundant Type Cast
Keeps the casting expression if the target is a lambda and the casting type is used for deriving the actual parameter types of the functional interface.
Keeps the casting expressions occurring in the parameters of an overloaded generic method invocation if the casting expression is used to determine which of the overloads is invoked.
# Reuse Random Objects
- Replaces
varwithRandomif the object that can be reused is defined using local variable type inference.
# Replace JUnit Expected Annotation Property with assertThrows
Prevents analyzing abstract methods.
# Use Functional Interfaces
Prevents converting an anonymous class into lambda in some cases where the method defined in the functional interface is generic.
# Verifying Third Party Libraries
Fixes a bug on parsing unusual, non-numeric version number suffixes of third-party libraries.
# Improvements
# Use Secure Random
The rule id changes from UseSecureRandomRule to UseSecureRandom.
# 3.26.0 21.01.2021
The 91st refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.26.0. The new rule helps migrating to JUnit 5.
# New Rule
# Replace JUnit Timeout Annotation Property with assertTimeout
The JUnit Jupiter API (opens new window) provides timeout assertions, i.e., assertions that make sure an executable completes before a timeout is exceeded.
In JUnit 4 this is achieved by using annotation properties, e.g., @Test(timeout=...).
This rule removes the timeout annotation property and inserts an assertTimeout (opens new window) instead.
# Fixed Bugs
# Classpath Conflict in OSGi Environment
- This fix overcomes a dependency conflict with a certain Eclipse plugin which was preventing jSparrow to validate the license key.
# 3.25.0 21.12.2020
The jSparrow 3.25.0 Christmas Release adds 5 more Free rules to jSparrow Starter:
- Remove Null-Checks Before Instanceof
- Use Optional::filter
- Collapse If Statements
- Use SecureRandom
- Use Offset Based String Methods
Now jSparrow Starter contains 20 Free Rules.
# 3.24.0 17.12.2020
The winter solstice jSparrow 3.24.0 release extends the rule set with three new refactoring rules.
# New Rules
# Replace JUnit ExpectedException with assertThrows
The ExpectedException.none() (opens new window) rule is deprecated since JUnit 4.13.
The recommended alternative is to use assertThrows() (opens new window).
This makes JUnit tests easier to understand and prevents scenarios where some parts of the test code are unreachable.
The goal of this rule is to make a transition from ExpectedException to testing exceptions with assertThrows.
# Replace JUnit Expected Annotation Property with assertThrows
Using the expected (opens new window) annotation property for testing the thrown exceptions is rather misleading.
Often it becomes unclear which part of the test code is responsible for throwing the exception.
This rule aims to overcome this problem by replacing the expected annotation property with assertThrows (opens new window) introduced in JUnit 4.13.
# Use Files.writeString
Java 11 introduced Files.writeString(Path, CharSequence, Charset, OpenOption...) (opens new window) and Files.writeString(Path, CharSequence, OpenOption...) (opens new window) for writing text into a file by one single invocation and in an efficient non-blocking manner.
This rule replaces BufferedWriters that are used to write a single value into a file, with Files.write(...).
Thus, achieving better performance when writing small files and improving the readability by removing code clutter.
# Fixed Bugs
# Support for macOS 11
- Fixes a bug that prevents the jSparrow License Check in macOS 11 Big Sur (opens new window).
# 3.23.0 19.11.2020
The 87th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.23.0. The new rule simplifies Comparator usages by making use of convenience methods added to the API in Java 8.
# New Rule
# Use Comparator Methods
Java 8 introduced new factory methods in the Comparator (opens new window) interface for simplifying the creation of Comparator instances.
This rule replaces lambda expressions representing comparators with simple invocations of Comparator factory methods, hence removing some code clutter and improving readability.
# Fixed Bugs
# New Imports Name Conflicts
- Prevents some conflicts that may arise when the name of a newly imported type coincides with the name of a local variable.
# 3.22.0 15.10.2020
The 86th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.22.0. It makes use of the Files.newBufferedWriter (opens new window) method for initializing BufferedWriter objects for writing to text to files.
# New Rule
# Use Files.newBufferedWriter
Java 7 introduced the Files (opens new window) class that contains convenience methods for operating on files.
This rule makes use of the Files.newBufferedWriter (opens new window) method for initializing BufferedWriter (opens new window) objects to write text files in an efficient non-blocking manner.
# Fixed Bugs
# Remove Unused Parameters in Private Methods
- Keeps the unused parameters that are annotated for DI or other purposes.
- Keeps the unused parameters if the method is pointed by a method reference.
# Use StringUtils Methods
- Fixes a bug related to identifying the version of the
apache.commons.lang(opens new window) library that is available in the project's classpath.
# Finding the Supported JLS Level
- Fixes a bug related to finding the latest JLS level supported by the Eclipse instance where jSparrow is running in.
# 3.21.0 17.09.2020
The autumn release of jSparrow 3.21.0 introduces 4 refactoring rules. This extends the total number of jSparrow rules to 85. Some improvements and bugfixes are also included.
# New Rules
# Create Temp Files Using Java NIO
A suitable alternative for creating temporary files in security-sensitive applications is to use java.nio.file.Files.createTempFile(String, String, FileAttribute<?>...) (opens new window) instead of java.io.File.createTempFile(String, String) (opens new window). The reason behind it is that files created by the former have more restrictive access permissions. This rule replaces the temporary file creation using java.io.File by the alternative methods defined in java.nio.file.Files.
# Use Files.newBufferedReader
Java 7 introduced the Files class that contains convenience methods for operating on files. This rule makes use of the Files.newBufferedReader (opens new window) method for initializing BufferedReader objects to read text files in an efficient non-blocking manner.
# Use Offset Based String Methods
This rule avoids creating intermediate String instances by making use of the overloaded offset based methods in the String API.
# Use Predefined Standard Charset
In order to avoid creating new objects, this rule replaces invocations of Charset.forName(String) (opens new window) by constants defined in StandardCharsets (opens new window).
# Fixed Bugs
# Escape User Input in SQL Queries
- Extends the scope of the rule by analyzing the variable holding the SQL query.
# Clean Up Third Party Dependencies
- Using some third party dependencies directly in the OSGi bundle classpath.
# 3.20.0 20.08.2020
The 80th and 81st refactoring rules are shipped with jSparrow 3.20.0. The goal of the new rules is to improve the unpredictability of random number generators. Some bugfixes and UI changes are also included.
# New Rules
# Reuse Random Objects
This rule extracts reusable java.util.Random objects from local variables to class or instance fields.
The goal is to improve the unpredictability of the generated values. Moreover, the rule reduces the number of objects created by the program.
# Use SecureRandom
This rule replaces pseudo-random number generators (PRNG), i.e., instances of Random (opens new window) with cryptographically strong random number generators (RNG), i.e., instances of SecureRandom (opens new window).
# UI Changes
# Summary Page
The jSparrow Summary page is redesigned to show which rules have been applied for each Java file.
# Preview Wizard
The jSparrow Preview wizard is updated to allow scrolling and source code selection in case the "Finish" button is enabled (this applies to the Free rules in jSparrow Starter and to all rules in jSparrow Pro (opens new window) and jSparrow Student (opens new window)). Otherwise, the changes in all files can be previewed through the "Change Navigation" controls, as highlighted in the animation below.
# Fixed bugs
# Use Parameterized JPA Query
- This fix allows the parameterization of the JPQL when the query string is stored in a local variable.
# Remove toString() on String
- Avoids removing
toString()in case it serves as the body of aConsumer<T>(opens new window).
# Use StringBuilder::append
- Avoids the StackOverflow errors thrown while refactoring string concatenations with an extremely large number of operands.
# Creating jSparrow Profiles
- This fix prevents creating or importing profiles named 'Custom'. This name is reserved for any arbitrary selection of jSparrow rules.
# Use Functional Interfaces
- Prevents refactoring in case the lambda expression candidate contains a reference to the field being currently initialized.
# 3.19.0 16.07.2020
The 79th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.19.0. It reduces security flaws by parameterizing the LDAP search filters.
# New Rule
# Use Parameterized LDAP Query
Similar to SQL queries, the LDAP (opens new window) search filters are also vulnerable to injection attacks. This rule parameterizes all potential user supplied input that are concatenated into an LDAP search filter.
# Fixed Bugs
# Make Fields And Variables Final
- Avoids throwing runtime exceptions in some cases when a field is initialized with a lambda expression.
# 3.18.0 18.06.2020
The midsummer release of jSparrow 3.18.0 adds three new rules to the ruleset and includes a few bugfixes.
# New Rules
# Use Parameterized JPA Query
It is a common misconception that JPA queries are immune to SQL injections, however, there are ways to secure them. This rule finds JPQL (opens new window) queries that are built by dynamically concatenating query fragments with potential user inputs and replaces them with parameterized JPQL queries. With this measure, the JDBC driver will escape input data before it is executed and therefore prevent SQL injection.
# Avoid Concatenation in Logging Statements
Replaces string concatenations passed in logging statements with built-in string formatting. This spares some needless computation in case the logging level is not low enough to show the message. Additionally, a built-in formatted string message improves the readability, too.
# Use Arrays Stream
Transforms Arrays.asList(T..values).stream() into an un-boxed specialized stream (i.e., IntStream (opens new window), LongStream (opens new window),
or DoubleStream (opens new window)) whenever possible.
Otherwise, the same stream generation is replaced with the shorthand method Stream.of(T... values) (opens new window).
# Fixed Bugs
# Make Fields And Variables Final
- Avoids converting a field to
finalif it is reassigned in the constructors or initializers of inner classes.
# Use Functional Interfaces
- Prevents transforming an anonymous class into a lambda expression in some cases where occurrences of the
thiskeyword refers to the instance of the anonymous class.
# StringBuffer() to StringBuilder()
- Prevents replacing a
StringBufferwith aStringBuilderin case the originalStringBuffervariable implicitly determines the type of the returned value.
# Replace For-Loop with Stream::forEach
- Fixes a corner case where the type boundaries of a generic lambda parameter could no longer be derived after the transformation.
# 3.17.0 20.05.2020
The 75th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.17.0. It reduces security flaws by escaping user supplied inputs concatenated with SQL queries.
# New Rule
# Escape User Inputs in SQL Queries
This rule detects potential user inputs that are concatenated with Oracle SQL queries and wraps them in ESAPI.encoder().encodeForSql(codec, input) (opens new window).
In this way, the contents of the user input will only be considered as values and not as code, thus preventing the SQL injection vulnerabilities.
# Fixed Bugs
# Use Functional Interfaces
- This fix relates to invocations of methods declared in Object class, default methods, and
thiskeyword when transforming anonymous classes to lambda expressions.
# 3.16.0 16.04.2020
The 74th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.16.0. It reduces security flaws by utilizing parameterized queries.
# New Rule
# Use Parameterized Query
This rule replaces a java.sql.Statement (opens new window) with a java.sql.PreparedStatement (opens new window) if the SQL query is constructed by concatenating string literals with user defined expressions (e.g. variables, method invocations, user input, etc).
Parameterized queries enforce a distinction between the SQL code and the data passed through parameters.
# Fixed Bugs
# Use Functional Interfaces
- Fixes unqualified field references when transforming an anonymous class into a lambda expression.
# 3.15.0 19.03.2020
jSparrow 3.15.0 extends the ruleset to 73 rules. Some UI improvements and Bug Fixes are also included.
# New Rules
# Use String Join
Replaces Collection::stream (opens new window) with
String::join (opens new window)
in cases where the sole purpose of the stream is to concatenate the String values of the collection.
# Remove Redundant Type Casts
Finds and removes casting expressions whose target types matches exactly the type of the original expression.
# Remove Collection::addAll
Moves the parameters used in Collection#addAll(Collection c) (opens new window)
to the constructor which is used for initializing a collection.
# UI improvements
# Starting jSparrow on Multiple Projects
jSparrow can be executed in multiple projects simultaneously either by selecting a parent project or by selecting more than one project on the project explorer.
# Sorting Results on the Summary Page
The results shown in jSparrow Summary Page can be sorted by the rule name, the number of findings or the time saved.
# Fixed Bugs
# Replace For-Loop with Enhanced-For-Loop
- If the
Iterableobject has been modified inside the loop body, the transformation would still have taken place.
# 3.14.0 20.02.2020
The 70th refactoring rule is shipped with jSparrow 3.14.0. It improves your java.util.Optionals.
# New Rule
# Use Optional::filter
This rule extracts an Optional::filter from the consumer used in Optional::ifPresent. This simplifies the lambda expression used with Optional operations.
# 3.13.0 30.01.2020
jSparrow 3.13.0 contains 69 refactoring rules now. The new rule improves your java.util.Optionals.
# New Rule
# Use Optional::map
This rule extracts an Optional::map from the consumer used in Optional::ifPresent. This makes complicated code blocks easier to read and reuse.
# Fixed Bugs
# Replace For-Loop with Enhanced-For-Loop
- If the loop variable has been used in the initialization expression of an inner loop, the variable name would have been dropped from this expression, rather than replaced properly.
# 3.12.0 19.12.2019
jSparrow 3.12.0 adds a new refactoring rule for improving source code readability. This brings jSparrow to a total of 68 automatic refactoring rules.
# New Rule
# Make Fields And Variables Final
This rule declares private fields and local variables final, if they are effectively final. Readability and maintainability of code is improved and accidental reassignments are prevented for affected fields and variables.
# 3.11.0 21.11.2019
jSparrow 3.11.0 brings you a new rule for enforcing coding conventions. It provides 67 automatic refactoring rules now.
# New Rule
# Hide Default Constructor In Utility Classes
Utility classes are classes containing static methods and fields only. Such classes should not be instantiated. The default constructor will be hidden by adding a private constructor to utility classes, which prevents their instantiation.
# 3.10.0 31.10.2019
In this release, jSparrow 3.10.0, we introduce a new rule for Java 9 and above.
# New Rule
# Use Optional::ifPresentOrElse
In Java 9, the Optional (opens new window) API has been extended with the Optional#ifPresentOrElse (opens new window) method. jSparrow replaces if-then-else statements, checking for Optional#isPresent (opens new window), with a single invocation of Optional#ifPresentOrElse (opens new window). This improves the readability of the code and enables the usage of higher order functions with Optional (opens new window).
# 3.9.0 19.09.2019
jSparrow 3.9.0 introduces a new automatic refactoring rule that improves performance in certain loops by eliminating redundant loop cycles.
# New Rule
# Insert Break Statements in For-loops
This rule finds Enhanced For-loops that return a boolean flag in case at least one element matches a certain criteria. In such cases, a break statement is added after the flag has been set the first time. This eliminates additional redundant loop cycles.
# 3.8.0 14.08.2019
With version 3.8.0 of jSparrow, two new refactoring rules are introduced. This brings jSparrow to a total number of 64 automatic refactoring rules!
# New Rules
# Use Collections Singleton List
Java offers an efficient way to create empty lists and single-element lists with Collections.emptyList() (opens new window) and Collections.singletonList(..) (opens new window) respectively. This rule searches for occurrences of Arrays.asList (opens new window) that can be replaced with either of those methods.
# Remove Null-Checks Before Instanceof
As seen in SonarCloud (opens new window), checks for null before instanceof can be redundant, since null cannot be an instance of anything. In logical conjunctions and disjunctions, this rule removes a null-check whenever it is redundant.
# 3.7.0 18.07.2019
The jSparrow 3.7.0 release contains a new refactoring rule and brings compatibility with Lombok (opens new window) annotations. Some stability improvements are also included.
# New Rule
# Replace For-Loop with Stream::takeWhile
Since Java 9, it is possible to get the prefix of a Stream with the takeWhile (opens new window) method.
This rule replaces enhanced for-loops iterating over the prefix of a collection with Stream::takeWhile.
# Lombok Compatibility
This release brings compatibility of jSparrow refactoring with Lombok (opens new window) annotations. The code generated by Lombok will not be affected by jSparrow.
# Fixed Bugs
# Replace Collection.sort with List.sort
- Allowing the transformation of
Collection.sorttoList.sortif the comparator is implemented inline as an anonymous class.
# 3.6.1 02.07.2019
# Hotfix Release
This hotfix release brings a bugfix on a refactoring rule.
# Fixed Bugs
# Use Local Variable Type Inference
- Allow converting the declared type to
varif the local variable is used as a parameter in overloaded methods.
# 3.6.0 19.06.2019
jSparrow 3.6.0 introduces three new refactoring rules.
# New Rules
# Use Factory Methods for Collections
Java 9 introduced a convenient way to create immutable collections with factory methods.
This rule, replaces the invocations of Collections.unmodifiableList/Set/Map with the corresponding factory method List.of (opens new window), Set.of (opens new window) and Map.ofEntries (opens new window) accordingly.
# Reorder Modifiers
This rule reorders the modifiers on Type, Field and Method Declarations based on the recommendation of Java Language Specification.
# Replace Collection.sort with List.sort
Java 8 introduced an extension to the List API by adding a sort (opens new window) method that sorts by Comparator. This rule replaces static invocations of Collections.sort(List, Comparator) with List.sort(Comparator).
# 3.5.1 23.05.2019
We have introduced a Customer Portal (opens new window), where you can report bugs and get support. There is also a new email address for customer support: support@jsparrow.io
This release adds the link to our Customer Portal and the new email address to the help dialogs in jSparrow.
# 3.5.0 16.05.2019
A new rule with the Old Language Constructs tag has been implemented for jSparrow 3.5.0. This brings jSparrow to a new total of 58 rules.
# New Rule
# Replace Map::get by Map::getOrDefault
This rule automatically replaces invocations of Map::get (opens new window) with the alternative Map::getOrDefault (opens new window), thus eliminating the succeeding null-checks.
# 3.4.0 18.04.2019
The jSparrow 3.4.0 release extends the the ruleset further with one more rule. Some stability improvements are also included.
# New Rules
# Remove Unused Parameters in Private Methods
This new rule finds and removes the unused parameters in private methods. As a result, all the references of the affected method are updated accordingly.
# Fixed Bugs
# StringBuffer() to StringBuilder()
- Avoid type incompatibilities in assignments and return statements when replacing a
StringBufferby aStringBuilder.
# 3.3.0 21.03.2019
The jSparrow 3.3.0 release brings a bunch of new rules, improvements to Java version handling, and some minor UI improvements.
# New Rules
# Use BufferedReader::lines
Replaces While-Loops and For-Loops that are using BufferedReader::readLine (opens new window) with streams using BufferedReader::lines (opens new window).
# Remove Modifiers in Interface Properties
Removes unnecessary modifiers on interface properties.
# Extended Rules
# Replace For-Loop with Stream::Match
In addition to Stream::anyMatch (opens new window), this rule is extended to allow converting Enhanced For-Loops to Stream::allMatch (opens new window) or Stream::noneMatch (opens new window).
# Java Version handling
Version resolution when running Eclipse with JDK 11 on Java 8 projects has been improved.
# UI Improvements
- Feedback when entering a license has been improved.
- License status in the jSparrow license preference page has been unified.
# 3.2.0 21.02.2019
# jSparrow Is Fit for Java 11
Since the official End of Life of Java 8 has been reached, we have updated jSparrow to be able to run on Java 11 as well as Java 8.
# New Rule
jSparrow 3.2.0 brings a new rule for collapsing if statements. The motivation behind this rule is to improve the readability of code by reducing the number of nested language constructs.
# Direct Link to Rule Documentation
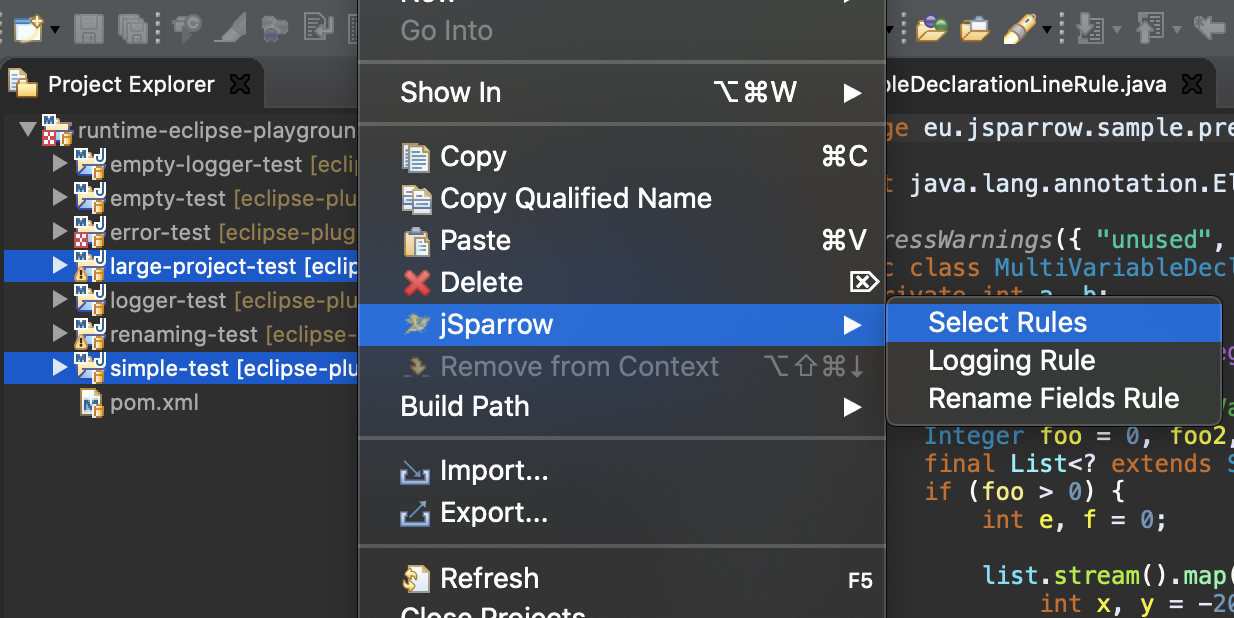
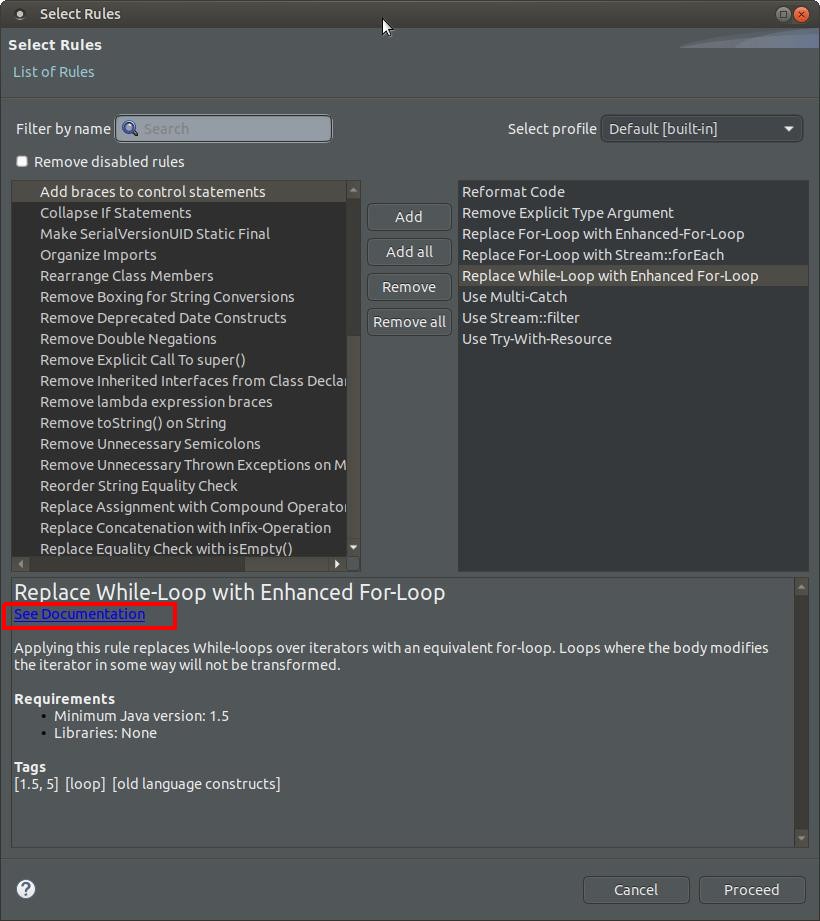
In the “Select Rules” wizard we have added a link to each rule description which leads directly to a detailed documentation of that rule on our website.
# 3.1.2 15.02.2019
# Hotfix Release
This hotfix release brings bugfixes on refactoring rules.
# Fixed Bugs
# Use Try-With-Resource
- Avoiding runtime exceptions when searching for the
Resource::close(opens new window) invocations.
# Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference
- Avoid creating method references on java arrays.
# 3.1.1 13.02.2019
# Hotfix Release
Resolving a connectivity failure in jSparrow Starter registration.
# Fixed Bugs
# jSparrow Starter Registration over proxy
- Fixes a bug related to the registration for jSparrow Starter in cases where the internet access is regulated with a proxy.
See also Define proxy in Eclipse.
# 3.1.0 29.01.2019
# jSparrow Lands on Eclipse 2018–12
Starting with version 3.1.0, jSparrow will be able be installed in Eclipse 2018-12.
# Old Welcome Screen Has Been Removed
The old welcome screen was removed due to the presence of the dashboard which allows you to stay up to date with dynamic content.
# Fixed Bugs
# Replace For-Loop with Stream::findFirst
- Identifying cases where the argument's type of the
orElseinvocation is not cast compatible with the stream type.
# Use Multi Catch
- Verifying that the types of the arguments in overloaded methods are not changed after merging the
catchclauses.
# Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference
- Avoiding ambiguities caused when converting a lambda expression to a method reference on an object with a raw type.
# Remove Lambda Expression Parenthesis
- Avoid introducing implicit return types when converting a lambda 'single-body-statement' (i.e., lambda statements whose body consist of a block with a single statement) to a lambda expression (i.e., a lambda statement whose body consist of a single expression).
# Replace static final Collections with Collections.unmodifiable...()
- Avoid converting a static final collection to an unmodifiable collection if it is used as an initializer of another collection.
# 3.0.0 21.12.2018
# Introduction of jSparrow Starter
Version 3.0.0 introduces jSparrow Starter!
This version of jSparrow makes it possible to apply 15 selected rules free of charge.
Registering enables jSparrow Starter permanently and allows you to apply the free rules without limitation.
# What does this mean exactly?
Previously, the free version of jSparrow showed possible changes, but did not have the finish button enabled. With jSparrow Starter, the finish button will be enabled for the free rules.
The original behavior of jSparrow Free remains unaffected.
# How to register?
See the documentation at: Registration for 15 free rules.
# List of free rules
- Replace For-Loop with Enhanced-For-Loop
- Organize Imports
- Use @Override Annotation
- Remove Boxing for String Conversions
- Remove Double Negations
- Remove toString() on String
- Remove Unnecessary Semicolons
- Remove Unnecessary Thrown Exceptions on Method Signatures
- Reorder String Equality Check
- Replace Equality Check with isEmpty()
- Replace equals() on Enum Constants
- Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference
- Replace Inefficient Constructors with valueOf()
- Split Multiple Variable Declarations
- Use Try-With-Resource
Note: All free rules have the tag "Free" added to them.
# Fixed Bugs
# Use StringUtils Methods
- Avoid implicit import collisions of 'StringUtils' classes from different packages.
# Replace For-Loop with Stream::findFirst
- Fixed an issue related to deriving the generic types of elements on a stream.
# System Out To Logging
- Finding the legal locations for using non-static loggers.
# Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference
- Using fully qualified names if it is not possible to add import statements.
- Avoiding ambiguities with overloaded methods when replacing lambdas by method references.
# Replace Concatenation with Infix-Operation
- Fixed an issue where the 'concat' method is not used for concatenating 'java.lang.String' instances.
# 2.7.0 21.11.2018
This release brings 6 new rules and a news dashboard.
# News Dashboard
A news dashboard has been added to jSparrow. Make sure to visit the dashboard regularly to get news on upcoming updates!
# New Rules
# Remove unnecessary thrown exceptions on method signatures
The following exceptions on method signatures are removed:
- Exceptions that are subtypes of already thrown exceptions
- Exceptions that are thrown more than once
- Exceptions that are inheriting from RuntimeException
See official documentation for more information: Remove Unnecessary Thrown Exceptions on Method Signatures
# Remove double negations
Removes pairs of negations from boolean expressions until only zero or one negation is left.
See official documentation for more information: Remove Double Negations
# Remove explicit call to super()
If a constructor does not explicitly invoke a superclass constructor, the Java compiler automatically inserts a call to the no-argument constructor of the superclass. Hence, there is no need to explicitly call the default constructor of the super class.
See official documentation for more information: Remove Explicit Call To super()
# Remove unnecessary semicolons
Finds and removes the unnecessary semicolons from the code blocks.
See official documentation for more information: Remove Unnecessary Semicolons
# Use StringBuilder::append
Replaces the infix operator + over String concatenations with at least three operands by StringBuilder::append. When possible, unwraps the parenthesized expressions.
See official documentation for more information: Use StringBuilder::append
# Use guard condition
Replaces, when possible, the last if-statement of a method body with a guard-if and unwraps its body.
See official documentation for more information: Use Guard Condition
# 2.6.0 21.09.2018
# Update Site Change
jSparrow has now different features for Neon/Oxygen and Photon. The jSparrow feature for Neon/Oxygen remains the same as before 2.6.0.
- Update can be done as before
The jSparrow feature for Photon is new and therefore it cannot be upgraded by the update mechanism from Eclipse.
- You need to install the the new feature from the Photon Category in at the Eclipse update site.
# New Rules
# Use local variable type inference
Minimum Java Version: 10 Replaces local variable declarations with var, wherever it is legal.
# Use Optional::ifPresent
Minimum Java Version: 8
Replaces if-clauses for Optionals with isPresent() by using the ifPresent(Consumer<? extends T>) method, which wraps the executing statements of the if clause into a Consumer.
# Fixed Bugs
# Reformat code rule replaces mutated vowels in constant strings
The reformat code rule was replacing mutated vowels with question marks within constant Strings. This behavior was corrected and the constant Strings remain unchanged.
# Compilation units with syntax errors stayed flagged as error afflicted classes even if the errors had been removed
Java classes with compilation errors are excluded from any refactoring by jSparrow by design. There has been a bug however, where fixing such Java classes with errors would still leave them marked to be ignored by jSparrow until Eclipse was restarted.
This issue has been fixed and Java classes will be evaluated for errors on each execution of jSparrow.
# 2.5.3 16.08.2018
The version range of the apache.commons.lang3 library that is used for the “Use StringUtils Methods” rule has been enlarged. Currently we support all versions that are released.
- Accepted versions of
apache.commons.lang3are now : [3.0,3.7]
# 2.5.2 31.07.2018
Eclipse Photon is now Supported
- Organize imports has been updates to work with Eclipse Photon
# 2.5.0 22.05.2017
This release brings substantial performance improvements, one new rule and various small improvements.
# Important Notice
License keys have to be added again! The way license information is stored changed. For this reason, all previously added license keys need to be added again. The license key can be added as follows: preferences → jSparrow → License → “Update license key”. We thank you for your understanding!
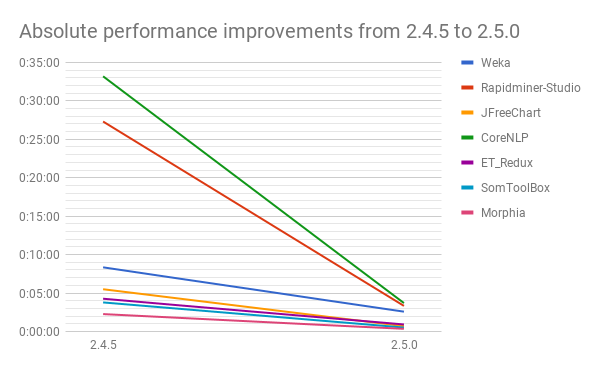
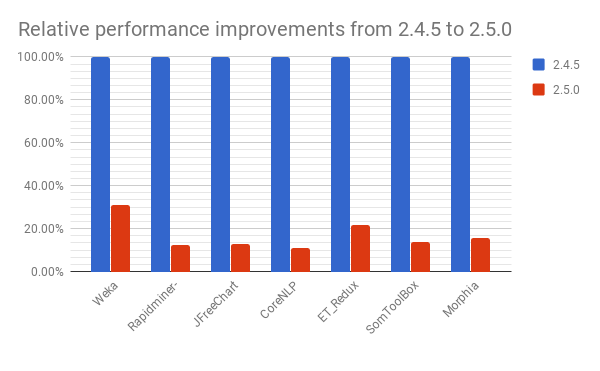
# Performance Improvements
Applying rules takes only half the time now!
Process improvements of the rule engine led to an overall reduced time for applying all refactorings in the “Select Rules” wizard. Measurements show that running jSparrow on projects only takes a fraction of the time it previously took.
# Remove Deprecated Date Constructs
Some java.util.Date constructors like new Date(int year, int month, int day), new Date(int year, int month, int date, int hrs, int min) and new Date(int year, int month, int date, int hrs, int min, int sec) are deprecated and the Calendar should be used instead. This rule searches for deprecated calendar instances, introduces calendar instances and sets the time corresponding to the parameters in the deprecated constructor, and replaces the latter with an invocation of Calendar.getTime(). For instance, the following code:
// Deprecated Date Constructor
Date date = new Date(90, 1, 31);
will be replaced with:
// Calendar instead of deprecated constructor
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(1990, 1, 31);
Date date = calendar.getTime();
Note that the date constructor is implicitly adding 1900 to the first argument (i.e. year), whereas Calendar.set is expecting the exact year value. Therefore, the rule takes care of preparing the parameters for the Calendar.set()-method properly.
If the deprecated constructor is used in a field initialization, then an initializing block is introduced for creating the calendar and initializing the field properly. See the before/after table.
# Removal of the Obsolete Field naming convention Rule
Since the introduction of the Rename Fields rule (Context Menu → jSparrow → Rename Fields Rule), the Field Naming Convention rule became obsolete. The Rename Fields rule offers more options and has better performance.
# Adjustment of the Time Saved
On the summary page the value of “Time Saved” now uses man-days, meaning eight-hour working days. Man-days are a more management-friendly unit than 24-hour working days and correspond better with current laws about working hours.
# MINOR UI IMPROVEMENTS
- Removal of the obsolete tag “logging”
- This tag is obsolete in the “Select Rules” wizard, since all logging related refactorings are bundled in the “Logging Rule” wizard.
- The “Add all” button is no longer enabled if only disabled rules are present
- Removal of the word “Apply” in the context menu
- Added a minimum width to the “Select Rules” wizard
- Bugfix to avoid UI freezes when committing survey results
- Bugfix that prevents a rare case where it was possible to select no profile
# 2.4.5 25.04.2018
# Bugfix for ImmutableStaticFinalCollections-Rule
Diamond Operators in Java 7 are not valid within a method parameter because their type cannot be inferred there. This caused a compilation error, when the rule was applied to a Java 7 project. The fix causes the rule to ignore collections in a Java 7 project, which use a Diamond Operator in their initializer.
# Bugfix for FieldRenaming-Rule
Solves an issue where the renaming of a field did not change the references to it in anonymous inner classes.
# 2.4.4 26.03.2018
Updated the way the free licenses work.
# Detailed Information
Free licenses have been reworked to no longer require a connection to the licensing server. When using older versions of jSparrow this might have led to warning issues. However, jSparrow functionality should not be adversely impacted. Any warnings should be able to be removed by upgrading to the latest version of jSparrow. If you experience errors that persist after the upgrade please contact us at bugreport@jsparrow.io.
# 2.4.3 20.02.2018
# Bug Fixes
- Further improvements on the comment preservation
- Minor improvements on the rule execution counting
- Duplicate profiles where possible if “x” was used to cancel the operation
- Using the “x” to abort the operation now behaves as expected
- jSparrow was executable on sub-elements of a class but was not executed because the types are not suitable for refactoring
- The visual display of jSparrow was removed from sub-elements of a class
# 2.4.2 30.01.2018
# Bug Fixes
- Fixed a bug where comments were lost in some cases.
# 2.4.1 09.01.2018
# Bug Fixes
- Fixed a bug where the number of times a rule was applied was displayed incorrectly.
- Fixed an issue that prevented some rules from counting the number of times they were applied correctly.
- Fixed a bug where changes made by the “Use Try-With-Resource” rule were not displayed under certain circumstances.
- Fixed a bug where no license warning was displayed if a license was already in use by another user.
# 2.4.0 19.12.2017
# Rename Fields Rule
This release adds a new semi-automatic rule called “Rename Fields Rule”.
This new rule can be used for finding and renaming the fields that do not comply with the Naming Conventions.
A configuration wizards provides different refactoring options. The user can select fields to be renamed based on the access modifier key (screenshot of the configuration wizard is given below). As soon as a field which doesn’t comply with the naming conventions is found, the rule will search for its references and compute a renaming. The search scope can be set by the user, either to the current project or to the workspace that eclipse is currently using.
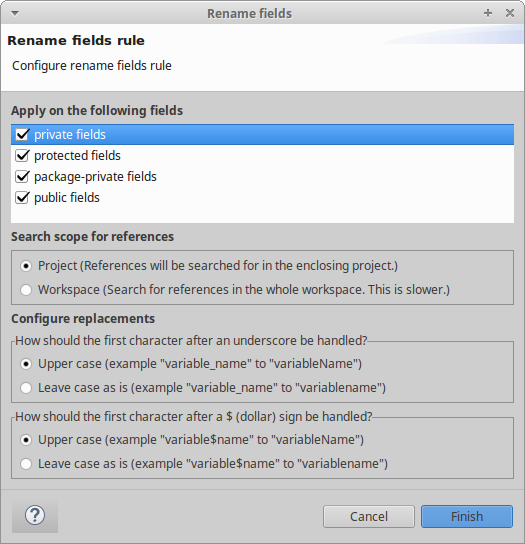
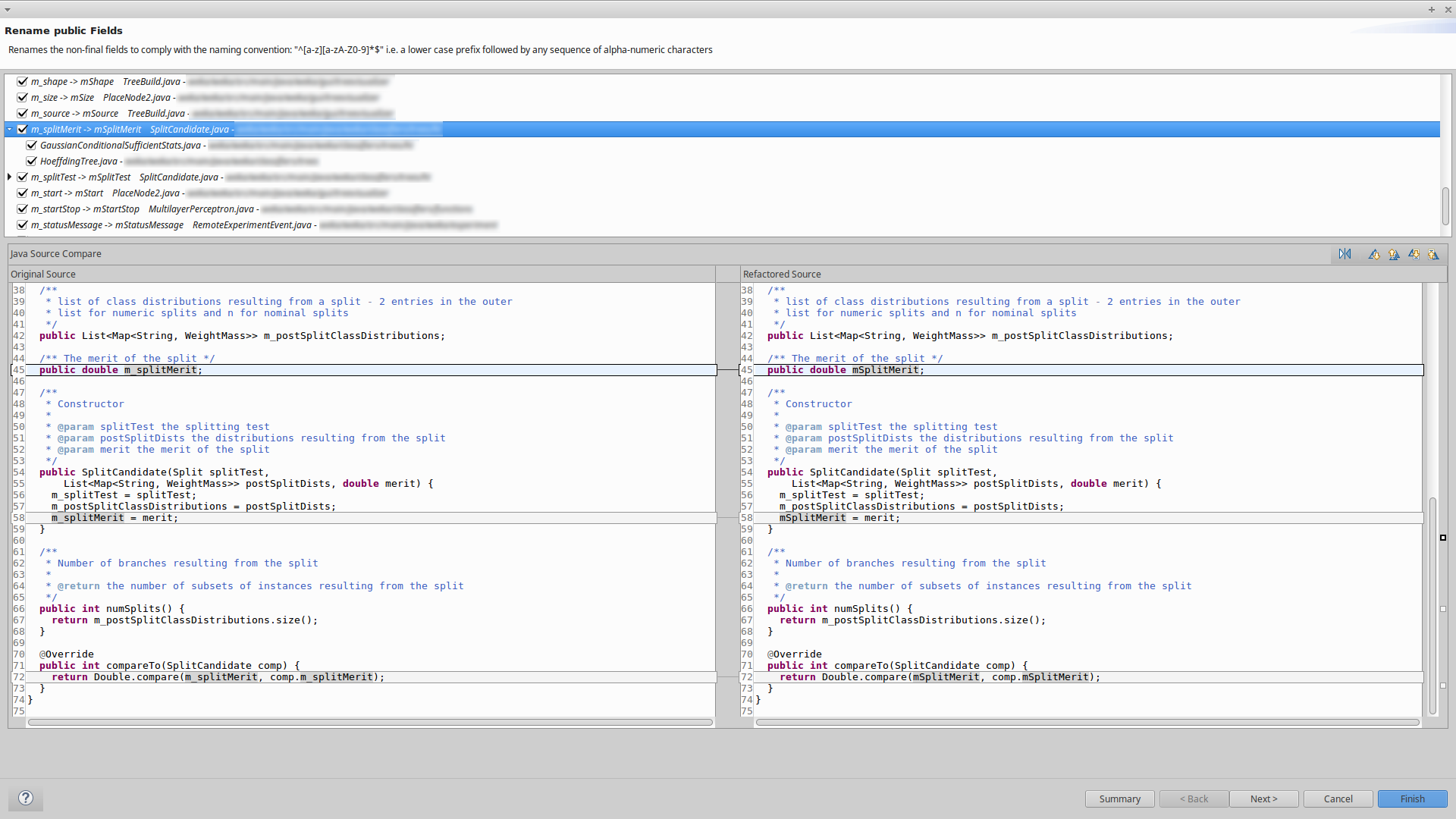
The new name is computed based on the existing field’ name and the configuration options that the user can provide on the rule wizard. On the default configuration, the existing field name is converted to camelCase. Furthermore the occurrences of underscores _ and dollar-signs $ are removed and the first letter which is following them (if any) is converted to uppercase. Note however, that the user has the possibility to choose in the configuration wizard whether or not to change the first letter after _ or $ to uppercase.
Before the renaming is applied to the original sources, a preview wizard will show the changes related to the renaming of each field. Since a non-private field may be accessed in multiple classes, a single renaming may affect more than one file. A tree-style view in the preview wizard will show the the changes to all of the affected files for each renaming. The user has the possibility to ignore a renaming by un-checking the corresponding element in the tree view.
Limitations
The renaming cannot be performed automatically if:
- The newly computed name is not a valid java variable name.
- The newly computed name clashes with an existing variable name within the same class.
# Bug Fixes
- Logging Rule:
- Fixed a bug where tooltips for checkboxes would not show up at the right position.
# 2.3.1 29.11.2017
# Bug Fixes
- Fixed a bug where controls on the Summary Page could be duplicated under certain circumstances.
- Fixed a bug where alphabetical sorting of files in the Summary page was disabled.
# 2.3.0 21.11.2017
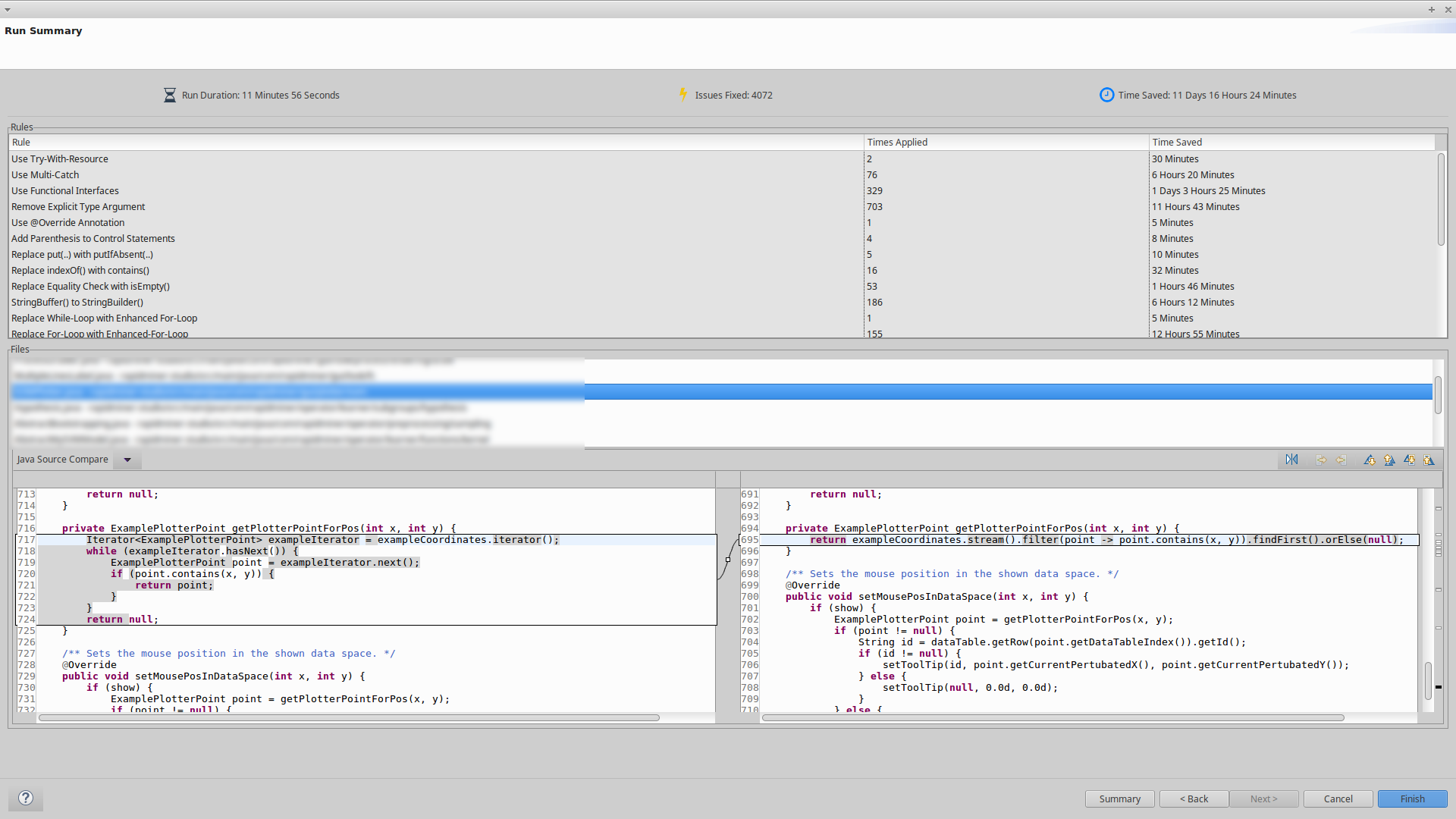
# Statistics
jSparrow now estimates the time it takes to fix issues. All rules in jSparrow get an individual estimation time to fix the corresponding issue. On each run of jSparrow, the time for each rule is multiplied by the number of occurrences of each corresponding rule, resulting in an estimation of saved time.
The statistics are added as follows:
(Updated) Preview Wizard: now additionally displays the following information for each rule individually:
- (New) Issues Fixed: The number of issues fixed for the current rule in all selected classes
- (New) Time Saved: The amount of time saved for the current rule in all selected classes
(Updated) Summary Page: now displays the following information for all rules:
- (New) Run Duration: The time it took jSparrow to get and calculate all changes (i.e., the time between clicking “Finish” in the “Select Rules” Wizard and the appearance of the Preview Wizard).
- (New) Issues Fixed: The overall number of fixed issues (i.e., how often rules were applied) for the current run of jSparrow.
- (New) Time Saved: The total time saved by applying all rules displayed.
- (New) Rules: A list of rules that were applied in the current run of jSparrow, including the number of times they were applied and the amount of time saved per rule.
- Files and Diff View: The complete list of files where jSparrow found potential changes and a diff view that displays changes for each file.
# Logging Rule
The Logging Rule has been updated in major ways to support more cases and provide greater customizability. The changes are focused on Exception logging.
(New) Logging Exceptions: A new grouping of Exception related logging options.
- (Updated) “Replace printStackTrace by a logger statement with selected level”
- Option to replace all occurrences of
printStackTracewith the selected severity level
- Option to replace all occurrences of
- (New) “Insert a logger statement with the selected level for unlogged exceptions”
- Option to add a logger statement to catch-clauses that do not log an Exception in any way
- (New) “Always add the exceptions as a parameter in logger statements”
- Option to always log an Exception if there is one present. For example, if only the message of an Exception is logged but not the Exception itself, the Exception will be added as additional argument to the log statement.
- (New) “Always use this severity level for logging exceptions”
- Option to always use the selected severity of “Logging Exceptions” when an Exception is logged, even though
System.out.printorSystem.err.printmight specify a different severity level.
- Option to always use the selected severity of “Logging Exceptions” when an Exception is logged, even though
- (New) Tooltips: Added examples for the checkboxes to illustrate the functionality
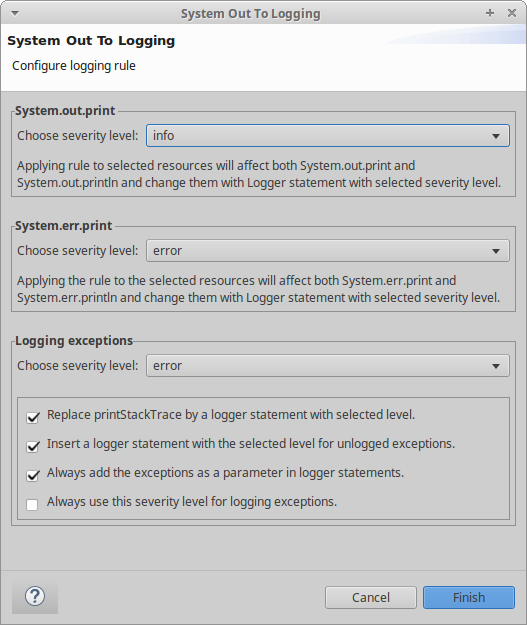
- (Updated) “Replace printStackTrace by a logger statement with selected level”
# Profile Settings
The profiles settings have been improved and jSparrow is now capable of importing and exporting rule profiles. Exported profiles are saved in YAML format.
(New) Import Profile(s)…
- Adds the functionality to import YAML formatted jSparrow profiles
(New) Export Profile(s)…
- Adds the functionality to export the selected profile(s) into a YAML formatted file

# New Rule: UsePutIfAbsent
This Java 8 rule updates the following old language construct and improves readability:
- If
map.put(..)is wrapped with a condition verifying the existence of an element one can usemap.putIfAbsent(…)instead.
# Usability Improvements
- Various usability improvements
- Option to switch between flat and recursive package resolving
- Re-selecting the same profile has the intended behavior of resetting the selected profiles
- Rule descriptions are now shown even on the right side of the Select Rules Wizard
# Bug Fixes
- Use Functional Interfaces:
- Fixed a NullPointerException that could occur under very specific circumstances
- Fixed an issue where a very specific case of an anonymous class containing wildcards in the body should not have been converted
- Replace Nested Loops with flatMap:
- Fixed an issue where more than two nested streams could not be converted to a
flatMap
- Fixed an issue where more than two nested streams could not be converted to a
- Use Multi-Catch:
- Fixed an issue where catch clauses were shifted below more generic Exceptions
- Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference:
- Fixed an issue where method references were incorrectly used for inner types
- Fixed an issue where jSparrow would not distinguish between
Integer.toString()andInteger.toString(Integer)
- Remove Explicit Type Argument:
- Fixed an issue where a Type Argument could not safely be inferred
- Replace static final Collections with
Collections.unmodifiable…():- Fixed an issue where unused imports where added
- Use StringUtils Methods:
- Fixed an issue where not all changes were added on the first run if a parameter of a method invocation was a method invocation that could also be transformed
- Rule tags:
- Fixed an issue where tags and “Remove disabled rules” would not work together
# 2.2.2 25.10.2017
# Bug Fixes
- Fixed a bug where Eclipse would report “Save Problems” when manually editing and saving files right after running jSparrow.
# 2.2.1 10.10.2017
# Bug Fixes
- An Issue was resolved if the project used Java 9 as language level.
- Replace For-Loop with Enhanced-For-Loop
- In cases the iterable was named after an primitive type with “s” as postfix the derived loop variable was translated to the corresponding primitive type. The behavior was changed so that an “a/an” is added as prefix to the created variable.
- Replace For-Loop with Enhanced-For-Loop
# 2.2.0 21.09.2017
This release is shipped with twelve new rules and other improvements to the user interface and the logic behind. In order to improve our possibility to track down bugs and other errors the OSGi bundle names have been changed. This has been necessary for jSparrow to work correctly with Eclipse Error Reporting. We have also added a new Summary Screen, where all changes can be reviewed before applying them. To make the selection of rules more intuitive and clearer we have changed their names to be more descriptive and consistent. The trial licensing model has been changed to accommodate new needs. Therefore it’s not possible anymore to persist changes with a trial license. However, changes can still be reviewed on the Summary Screen.
# Names of the OSGi Bundles Have Been Changed
- The prefix of the OSGI-bundles and OSGi-features of jSparrow has been changed from:
jSparrow→eu.jSparrow - Important: The result is that it is not possible to update from a previous version of jSparrow! It is required to uninstall and reinstall jSparrow to upgrade to 2.2.0. Otherwise there might be side effects because there will be two different named instances of jSparrow within your Eclipse version.
# Trial Licensing Model Changed
- The trial license has changed.
- The major change is that it’s no longer possible to apply changes to source code.
- All changes will be displayed by the Preview Wizard and a Summary is shown in the final step at the new Summary Page.
# Summary Page
- Introduction of a Summary Page that displays all the changes from all rules that will be made.
# New Rules Have Been Added
- Remove Inherited Interfaces from Class Declaration
- Remove interfaces from class declaration, which are already implemented by a super class. These interfaces are inherited from the super class.
- Replace Equality Check with
isEmpty()- Java 6 introduced
isEmpty()onCollectionsandStrings. This rule replaces equality checks involvinglength()orsize()with calls toisEmpty(). For example,s.length() == 0becomess.isEmpty(). Applying this rule improves readability.
- Java 6 introduced
- Replace
equals()on Enum constants- Replace occurrences of
equals()on Enum constants with an identity comparison (==). In the case the equals relation is wrapped with an boolean negation the result will be an not equals (!=).
- Replace occurrences of
- Replace For-Loop with
Stream::anyMatch- Replaces an occurrences of enhanced for-loops which are only used to initialize or return a boolean variable with
Stream::anyMatch. The stream syntax is more concise and improves readability.
- Replaces an occurrences of enhanced for-loops which are only used to initialize or return a boolean variable with
- Replace For-Loop with
Stream::collect(Collectors.joining())- Transforms loops which are only used for concatenating a
Stringto an invocation ofStream::collect(Collectors.joining()). If the Java compliance level is below 1.8 and at least 1.5, then aStringBuilderis introduced for concatenating the values on each iteration of the loop.
- Transforms loops which are only used for concatenating a
- Replace For-Loop with
Stream::findFirst- Enhanced for-loops which are used to find an element within a collection can be replaced by
Stream::findFirst. Using the stream syntax a multi-line control statement can be reduced to a single line.
- Enhanced for-loops which are used to find an element within a collection can be replaced by
- Replace For-Loop with
Stream::sum- Transforms enhanced for-loops which are only used for summing up the elements of a collection to a
Stream::suminvocation
- Transforms enhanced for-loops which are only used for summing up the elements of a collection to a
- Replace
indexOf()withcontains()- This rule replaces calls to
indexOf()on instances ofStringor Collection with calls to thecontains()method. For examplel.indexOf(s) >= 0is transformed tol.contains(s).contains()was introduced in Java 1.4 and helps to make the code more readable.
- This rule replaces calls to
- Replace Nested Loops with flatMap
- Nested For-Loops or invocations of forEach commonly used to iterate over all elements of a collection of collections, can be avoided by using
flatMap(). UsingflatMap()makes code much more readable and can be combined with other stream functions.
- Nested For-Loops or invocations of forEach commonly used to iterate over all elements of a collection of collections, can be avoided by using
- Replace static final Collections With Collections.unmodifiable…()
- An unmodifiable Collection can be created with the matching
Collections.unmodifiable…()method. Some examples areCollections.unmodifiableList(),Collections.unmodifiableSortedSet(), etc. A declaration of aCollectionwith thestaticandfinalmodifiers is not sufficient because it might still be modifiable. TheCollectionswhich are created withCollections.unmodifiable…()throw anUnsupportedOperationExceptionas soon as a modification is attempted.
- An unmodifiable Collection can be created with the matching
- StringBuffer() to StringBuilder()
- This rule changes the type of local variables from
StringBuffer()toStringBuilder().
- This rule changes the type of local variables from
- Use equals() on Primitive Objects
- It is recommended that you use
equals()on primitive objects. Applying this rule will replace occurrences of!=and==withequals(). For example,”hello” == “world”will become”hello”.equals(“world”)Using this rule helps to avoid bugs, as==checks for object reference equality instead of value equality.
- It is recommended that you use
# Name Changes of Rules
| Previous Name | Current Name |
|---|---|
| Arithmetic Assignment | Replace Assignment with Compound Operator |
| Braces to Control-Block | Add Parenthesis to Control Statements |
| Collection removeAll() to clear() | Replace removeAll() with clear() |
| Use Diamond Operator | Remove Explicit Type Argument |
| Enhanced For-Loop to Stream::forEach | Replace For-Loop with Stream::forEach |
| Field names convention | Apply Field Naming Conventions |
| For to ForEach | Replace For-Loop with Enhanced-For-Loop |
| Use FunctionalInterface | Use Functional Interfaces |
| Replace constructors of primitive types with valueOf() method | Replace Inefficient Constructors with valueOf() |
| Stream forEach to collect | Use Stream::collect |
| if-Wrapper in Stream::forEach to Stream::filter | Use Stream::filter |
| Lambda forEach to map | Use Stream::map |
| Expression Lambda to Method Reference | Replace Expression Lambda with Method Reference |
| MultiCatch | Use Multi-Catch |
| Separate lines for variable declarations | Split Multiple Variable Declarations |
| OrganiseImportsRule | Organize Imports |
| @Override annotation rule | Use @Override Annotation |
| SonarQube: Primitives should not be boxed just for String conversions | Remove Boxing for String Conversions |
| Rearrange class members | Rearrange Class Members |
| Remove new String() constructor | Remove String Constructor |
| Remove toString() from Strings | Remove toString() on String |
| SerialVersionUid check for static, final | Make SerialVersionUID Static Final |
| Standard Logger | System Out To Logging |
| Statement Lambda To Expression Lambda | Remove Lambda Expression Parenthesis |
| Replace String.concat(param) with Infix-Operation Plus | Replace Concatenation with Infix-Operation |
| String.format() System line separator | Use Portable Newline |
| String Literals equality check | Reorder String Equality Check |
| StringUtils | Use StringUtils Methods |
| TryWithResource | Use Try-With-Resource |
| While-loops to for-loop | Replace While-Loop With Enhanced For-Loop |
# 2.1.0 14.08.2017
- New welcome screen that explains in very short terms how to use jSparrow, including a feedback area
- A new license expired dialog with a feedback form
- Improved dialogs for error messages
- Improvement of the forEach to Lambda rule
- Minor bugfix of the Lambda do method reference rule
# 2.0.2 06.07.2017
- Support for Eclipse Oxygen
- Support for macOS
# 2.0.0 21.06.2017
- UI improvements
- Redesign of the selection process within the corresponding wizard
- Redesign of the preference page
- profiles have been improved
- General
- Introduction of rule requirements
- Introduces a background check that is performed on the selected sources, respectively the project they are located in, to check different requirements
- Java version requirement check added
- Required libraries check added
- Introduction of interactive rules
- SystemOutToLogging rule was introduced which requires addition user interaction to be executed
- Introduction of rule requirements
- Ruleset Additions
- Target Java 1.0 and upwards
- Rearrange class members
- Class elements are sorted according to the oracle code convention for file organization
- Order of visibility modifieres are also included
- Yoda Conditions for Strings
- Constants are moved to the left side of the condition to prevent an accidental assignment
- Naming conventions for private elements
- Change names of variables according to Java code conventions of Oracle
- Multiple variables should not be declared in the same line
- Splitting the variable declaration to multiple lines to prevent implicit changes on multiple variables, by changing the modifier of one line.
- Interactive Rule: System out to logging
- Introduces the replacement of System.out statements (
println,error,e.printstacktrace) with a logging statement- Requires the configuration of a logging environment (log4j, slf4j)
- Introduces the replacement of System.out statements (
- Rearrange class members
- Target Java 1.6 and upwards
- @Override addition
- To improve readability and enforcing compile errors on methods where the signature has changed the
@Overrideannotation should be applied
- To improve readability and enforcing compile errors on methods where the signature has changed the
- @Override addition
- Target Java 1.7 and upwards
- Diamondrule
- Removes unnecessary generic type references to replace them with diamonds
- Diamondrule
- Target Java 1.8 and upwards
- Lambda statements to method references
- Replaces Java 8 lambda function definitions with a method reference lambda if possible
- Statement lambda to expression
- If the body of the lambda statement contains only a single expression, the braces are optional. It is reduced to a lambda expression.
- For Each to Lambda
- Transforms a for each loop to a corresponding lambda statement
- Addition Optimization possibilities for lambda loops
- if-statements without else to filters from streams
- unwrapping object done with mapping from streams
- collecting objects done with collect from streams
- Lambda statements to method references
- Target Java 1.0 and upwards
# 1.1.0 31.03.2017
- Support for Eclipse Mars
- UI improvements
- Addition of progress monitors for better feedback
- Loading indicators on various points where real time background processing is not possible
# 1.0.0 01.02.2017
- Support for Eclipse Neon
- Support for Ubuntu and Windows 7/10
- Execution on different views in the Eclipse IDE
- Editor
- Package Explorer
- Introduction of a diff-view after application of the selected rules
- Contains Preference Page to customize the behavior.
- Initial Ruleset
- Target Java 1.0 and upwards
- OrganiseImports
- Removes unused imports and organizes them
- StringUtils
- Apache Commons Lang
StringUtilsrequired in classpath of executing project - Replaces operations on
Stringobject with correspondingStringUtilsoperation
- Apache Commons Lang
- OrganiseImports
- Target Java 1.1. and upwards
- SerialVersionUid
- Adds the modifieres
staticandfinaltoSerialVersionUidlong variables when they are absent
- Adds the modifieres
- RemoveNewStringConstructor
- Removes all class instantiations from
Stringif its parameter is empty or aString.
- Removes all class instantiations from
- RemoveToStringOnString
- Removes all method invocation of
toString()on aStringobject
- Removes all method invocation of
- StringConcatToPlus
- Replaces the
Stringconcatenation with the method invocation with the plus operation forStrings
- Replaces the
- PrimitiveBoxedForString
- A boxed primitive is allocated just to call
toString(). It is more effective to just use thestaticform oftoStringwhich takes the primitive value.
- A boxed primitive is allocated just to call
- InefficientConstructor
- All calls to a constructor of a primitive type will be replaced by the corresponding static
valueOf()method.
- All calls to a constructor of a primitive type will be replaced by the corresponding static
- ArithmeticAssignment
- Assignments that only execute simple arithmetic operations on the target are resolved as arithmetic assignment
- BracketsToControl
- All control flow statements that aren’t using curly braces are wrapped to improve readability
- SerialVersionUid
- Target Java 1.2 and upwards
- CollectionRemoveAll
- Collections that use remove all elements by applying it to itself could also be cleared.
- use
collection.clear()instead ofcollection.removeAll(collection)
- CollectionRemoveAll
- Target Java 1.5 and upwards
- WhileToForEach
- Replaces while loops with for-each loops that have been introduced in Java 1.5
- ForToForEach
- Replaces traditional for loops with for-each loops that have been introduced in Java 1.5
- StringFormatLineSeparator
- Use
String.formatplaceholder for linebreak instead of distribution system dependent linebreak.
- Use
- WhileToForEach
- Target Java 1.7 and upwards
- MultiCatch
- Combines multiple catch phrases that handle the error identically
- MultiCatch
- Target Java 1.0 and upwards